Thermostat for radiators
Sometimes it becomes necessary to adjust the temperature in each specific room. This can be done by installing a thermostat for a heating radiator. This is a small device that regulates the heat transfer of the radiator. Can be used with all types of radiators, except cast iron. One important point - the device can lower the initial temperature, but if there is not enough heating power, it cannot increase it.
The content of the article
The design of thermostats for heating radiators
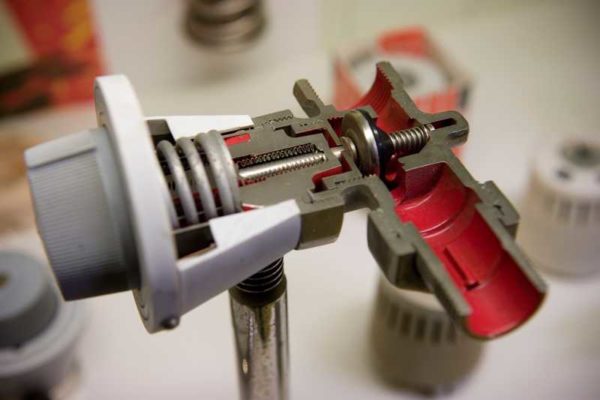
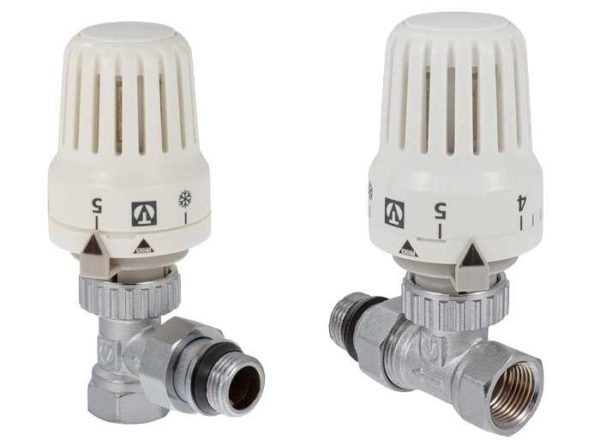
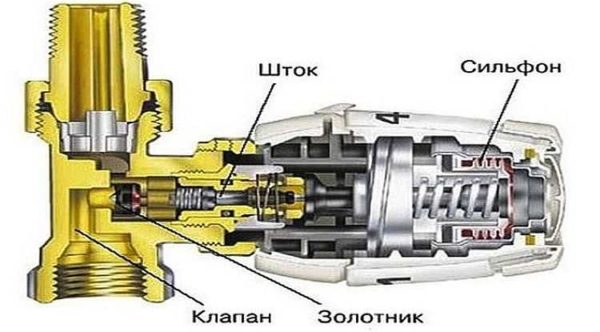
The thermostat for a heating radiator consists of two parts - a valve (thermo valve) and a thermostatic head (thermostatic element, temperature controller). These products are produced for different pipe sizes and different types of heating systems. The thermostatic head is removable, regulators of different types and even different manufacturers can be installed on the same valve - the seat is standardized.

Thermostat for a heating radiator consists of two parts - a special valve (valve) and a thermostatic head (regulator)
Both valves and regulators are different, so before installing a thermostat for a heating radiator, you will have to get at least a little familiar with its structure, functions and types.
Thermal valve - structure, purpose, types
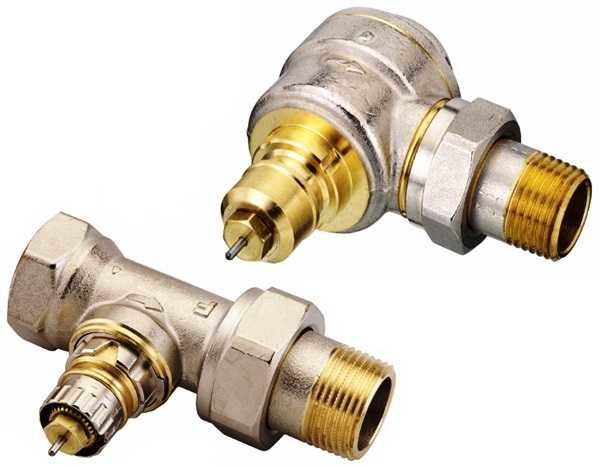
A valve in a thermostat is very similar in structure to a conventional valve. There is a seat and a shut-off cone that opens / closes the lumen for the flow of the coolant. The temperature of the heating radiator is regulated in exactly this way: by the amount of the coolant passing through the radiator.
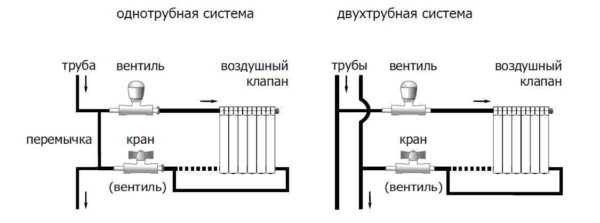
Different valves are installed on one-pipe and two-pipe valve wiring. The hydraulic resistance of the valve to a single-pipe system is much lower (at least twice) - this is the only way to balance it. You cannot mix up the valves - it will not heat. For systems with natural circulation, valves for one-pipe systems are suitable. When installed, the hydraulic resistance, of course, increases, but the system will be able to work.
Each valve has an arrow indicating the movement of the heating medium. When installing, it is installed so that the direction of flow coincides with the arrow.
What materials
The valve body is made of corrosion-resistant metals, often additionally coated with a protective layer (nickel-plated or chrome-plated). There are valves from:
- bronze (nickel and chrome plated);
- brass (covered with a layer of nickel);
- of stainless steel.
It is clear that stainless steel is the best option. It is chemically neutral, does not corrode, does not react with other metals. But the cost of such valves is high and difficult to find. Bronze and brass valves are approximately the same in terms of service life. What is important in this case is the quality of the alloy, and well-known manufacturers carefully monitor it. Whether or not to trust the unknown is a moot point, but there is one point that is better to track. An arrow must be present on the body to indicate the direction of flow. If it is not there, this is a very cheap product, which is better not to buy.
By way of execution
Since radiators are installed in different ways, the valves are made straight (straight through) and angled. Choose the type that will improve your system.
| Name / company | For which system | Du, mm | Body material | Operating pressure | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danfos, angular RA-G, customizable | one-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 25-32 $ |
| Danfos, straight RA-G, customizable | one-pipe | 20 mm, 25 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 32 - 45 $ |
| Danfos, angular RA-N adjustable | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm. 25 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 30 - 40 $ |
| Danfos, straight RA-N configurable | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm. 25 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 20 - 50 $ |
| BROEN, straight with fixed setting | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 8-15 $ |
| BROEN, straight with fixed setting | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 8-15 $ |
| BROEN, corner adjustable | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 10-17 $ |
| BROEN, corner adjustable | two-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 10-17 $ |
| BROEN, straight with fixed setting | one-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 19-23 $ |
| BROEN, angular fixed setting | one-pipe | 15 mm, 20 mm | Nickel plated brass | 10 bar | 19-22 $ |
| OVENTROP, axial | 1/2" | Nickel-plated brass, enamelled | 10 bar | 140 $ |
Thermostatic heads
There are three types of thermostatic elements for heating thermostats - manual, mechanical and electronic. They all perform the same functions, but in different ways, provide different levels of comfort, and have different capabilities.
Manual
Manual thermostatic heads work like a regular tap - turn the regulator to one side or the other, letting in more or less coolant. The cheapest and most reliable, but not the most convenient device. To change the heat transfer, you must manually turn the valve.
These devices are quite inexpensive, they can be installed at the inlet and outlet of the heating radiator instead of ball valves. Any of them can be regulated.
Mechanical
A more complex device that maintains the set temperature in automatic mode. The basis of this type of thermostatic head is a bellows. It is a small elastic cylinder filled with a thermal agent. A thermal agent is a gas or liquid that has a high coefficient of expansion - when heated, they greatly increase in volume.
The bellows supports the stem that covers the flow area of the valve. Until the material in the bellows is heated, the stem is raised. As the temperature rises, the cylinder begins to increase in size (gas or liquid expands), it presses on the rod, which is increasingly blocking the flow area. Less and less coolant passes through the radiator, it gradually cools down. The substance in the bellows also cools down, due to which the cylinder decreases in size, the rod rises, more coolant passes through the radiator, it starts to warm up a little. Then the cycle is repeated.
Gas or liquid
In the presence of such a device, the temperature in the room is fairly maintained at exactly + - 1 ° C, but in general the delta depends on how inert the substance in the bellows is. It can be filled with some kind of gas or liquid. Gases react faster to temperature changes, but they are more difficult to produce technologically.
Fluids change volumes slightly more slowly, but are easier to manufacture. In general, the difference in the accuracy of maintaining the temperature is about half a degree, which is almost impossible to notice. As a result, most of the presented thermostats for heating radiators are equipped with thermal heads with liquid bellows.
With remote sensor
The mechanical thermostatic head must be installed so that it is directed into the room. This way the temperature is measured more accurately. Since they are fairly large in size, this installation method is not always possible.For these cases, you can supply a thermostat for a heating radiator with an external sensor. The temperature sensor is connected to the head using a capillary tube. You can position it at any point where you prefer to measure the air temperature.
All changes in the heat transfer of the radiator will occur depending on the air temperature in the room. The only drawback of this solution is the high cost of such models. But the temperature is maintained more accurately.
| Name / company | Setting range | Operating temperature range | Control type | Functions / purpose | Connection type | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danfoss living eco | 6 ° C to 28 ° C | 0 ° C to 40 ° C | Electronic | Programmable | RA AND M30X1.5 | 70$ |
| Danfoss RA 2994 with gas bellows | 6 ° C to 26 ° C | 0 ° C to 40 ° C | Mechanical | For any radiators | clip-on | 20$ |
| Danfoss RAW-K w / liquid earphone | 8 ° C to 28 ° C | 0 ° C to 40 ° C | Mechanical | For steel panel radiators | M30x1.5 | 20$ |
| Danfoss RAX with liquid earphone | 8 ° C to 28 ° C | 0 ° C to 40 ° C | Mechanical | For design radiators white, black, chrome | M30x1.5 | 25$ |
| HERZ H 1 7260 98 with liquid earphone | 6 ° C to 28 ° C | Mechanical | M 30 x 1.5 | 11$ | ||
| Oventrop "Uni XH" with liquid earphone | 7 ° C to 28 ° C | Mechanical | with zero mark | M 30 x 1.5 | 18$ | |
| Oventrop "Uni CH" with liquid earphone | 7 ° C to 28 ° C | Mechanical | without zero mark | M 30 x 1.5 | 20$ |
Electronic
The electronic thermostat for a heating radiator is even larger in size. The thermostatic element is even larger. In addition to electronic filling, two batteries are also installed in it.
In this case, the movement of the stem in the valve is controlled by a microprocessor. These models have a fairly large set of additional functions. For example, the ability to set the room temperature by the clock. How is it fashionable to use it? Doctors have long proven that it is better to sleep in a cool room. Therefore, at night you can program the temperature lower, and in the morning, when it’s time to wake up, it can be set higher. Conveniently.
The disadvantages of these models are their large size, the need to monitor the discharge of the batteries (enough for several years of operation) and the high price.
How to install correctly
They put a thermostat for a heating radiator at the inlet or outlet of the heater - there is no difference, they work with equal success in both positions. How to choose a place to install?
At the recommended installation height. There is such an item in the technical specifications. Each device is factory set - calibrated for temperature control at a specific height and usually this is the upper radiator manifold. In this case, the heat regulator is installed at a height of 60-80 cm, it is convenient to adjust it manually if necessary.
If you have a bottom saddle connection (pipes fit only from the bottom), there are three options - look for a device that can be installed at the bottom, put a model with an external sensor, or reconfigure the thermal head. The procedure is simple, the description should be in the passport. All you need is to have a thermometer and turn the head at certain moments in one direction, then in the other direction.
The installation process itself is standard. The valve has a thread. Suitable fittings are selected for it or a counter thread is cut on a metal pipe.
One important point to keep in mind for those who want to install a thermostat for a heating radiator in apartment buildings. If you have one-pipe wiring, they can be installed only if there is a bypass - a section of pipe that stands in front of the battery and connects two pipes together.

If you have a similar wiring (there may not be a pipe on the right), a bypass is required. Place the thermostat immediately behind the radiator
Otherwise, you will regulate the entire riser, which will definitely not please your neighbors. For such a violation, a very substantial fine can be issued. Therefore, it is better to put a bypass (if not).
How to adjust (readjust)
All thermostats are factory set. But their settings are standard and may not match your desired parameters. If something does not suit you at work - you want it to be warmer / colder, you can reconfigure the thermostat for the heating radiator. This must be done when the heating is running. You need a thermometer. You hang it at the point where you will control the state of the atmosphere.
- Close the doors, put the thermostat head in the extreme left position - completely open. The room temperature will start to rise. When it becomes 5-6 degrees higher than what you want, turn the regulator all the way to the right.
- The radiator starts to cool down. When the temperature drops to a value that you think is comfortable, begin to slowly turn the knob to the right and listen. When you hear that the coolant is noisy, and the radiator begins to warm up, stop. Remember which number is on the handle. It will need to be set to reach the required temperature.
It is not difficult to adjust the thermostat for the radiator. And you can repeat this action several times by changing the settings.



















I didn't quite understand then. If I put it in the extreme left position (fully open), then it closes for me when the temperature reaches 22-24 degrees (as per the technical data sheet). How can I make the temperature higher and then I can set 26-28 at 5 mode?
my valve closes when the temperature reaches 23-24 degrees (mode 5). How can I make the temperature higher and then I can set 26-28 at 5 mode?
Can you please tell me if a thermostatic valve can be installed in a heating system with natural circulation? And if so, which thermostatic valve is right?