Threaded pipe connection: types, parameters, designation, tables of pipe thread sizes
We often find carving and there are many types of it. For example, on fasteners - bolts, studs, nuts - turns of the same type. Another is applied to the pipes. The main property of pipe threads is that it gives a tight connection. This is exactly what is required in pipelines in relation to pipe threads. We will consider it in more detail.
The content of the article
What is thread and its types
A thread is a groove of a special shape and size, spirally applied to the inner or outer surface of a pipe or metal rod. Can be applied to cylindrical or tapered surfaces. It is characterized and differs from each other by the shape of the groove, the height / depth of the relief and the distance between the turns - the pitch. In order to connect two parts, they must have the same or compatible thread, with one part having an external thread, the other with an internal thread of the same type and size.
In general, threads are divided into fastening and running threads. Undercarriages are used in the elements of machines and provide movement. We are more interested in those that are used in everyday life and that we encounter in the process of repair and construction. This is just the fastening thread. In fact, we will talk about it.
It is also worth knowing that in the direction of applying the turns, the threads are right and left, and on the surface on which they are applied - cylindrical and conical.
Types of threads
The pipe thread has its own profile, which gives tightness. It serves for non-welded connection of metal pipes in pipelines, installation of all kinds of fittings, connection of devices. Recently, a threaded connection has also been used on some types of plastic pipes, but the approach is different there - it is cast, although the essence is the same.
There are three main types of threads:
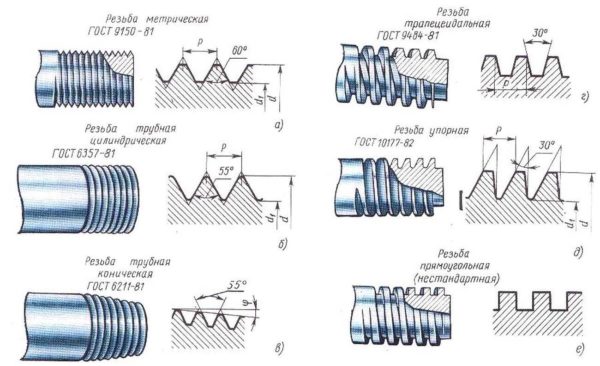
- Metric. It can be distinguished by the sharp tops of the turns and grooves. The shape is a triangle with angles of 60 °. It is named so because its parameters are indicated in millimeters, and these are the units of the metric system. Standardized by GOST 9150-81.
- Inch. It is also based on a triangle, but with an apex of 55 °. It is present on imported parts. As you can see, the difference between metric and tapered threads in the corners.
- Pipe. It differs from metric in a slightly smaller angle - 55 °, and with an inch it has the same angle. The main difference is that the faces are rounded. And this is fundamentally important. It can be applied to a cylinder (pipe), and then the word "cylindrical" is added to the name. Standardized by GOST 6357-81. When tapping on a taper, it is called a tapered pipe thread.
The types of threads that can be on imported fittings and accessories may also come in handy. This is a Whitworth thread and is designated BSW for coarse pitches and BSF for fine pitches. It was this standard that was taken as a basis for the development of pipe threads in the USSR. So Whitworth threads and pipe threads made to standard are compatible.
There are other profiles as well, but they belong to running gear and are very specific. Not needed under normal conditions. For general development, let's say that there are also rectangular and trapezoidal shapes.
Where which one is used
Now about where what type of thread is used. Metric is applied to anchors, bolts, studs, nuts and other fasteners.Applied to a cylindrical surface does not provide tightness, therefore, it is not the best choice for pipelines. However, it is used, and for tightness it is put on a reel - tow or fum tape. In addition to plumbing, it is used when assembling frames from round pipes on a threaded connection.
The picture changes when a metric thread is applied to a tapered surface. This connection has a high degree of tightness. It is the metric tapered thread that is applied to the covers, is used in industrial pipelines, for the transportation of gas and liquids that emit volatile substances. In everyday life, the use of tapered threads is limited, since special equipment is required for its application.
It is not hard to guess that pipe threads are used in pipelines. Thanks to the smooth profile lines, even without additional sealing, the connection is tight. It is this type that is applied on squeegees, corners, tees, and other devices that are used in the assembly of water supply, heating and sewerage systems.
Types of pipe threads
So, what is pipe thread. This is the one that has grooves of a special profile. It is based on a triangle with a 55 ° apex and rounded corners. The symbol is G, after which the nominal pipe bore is indicated in inches. That is, G 1 1/2 ″ is used in the drawings. This will mean that the connection is threaded, pipe thread with a nominal diameter of 1 1/2 inches.
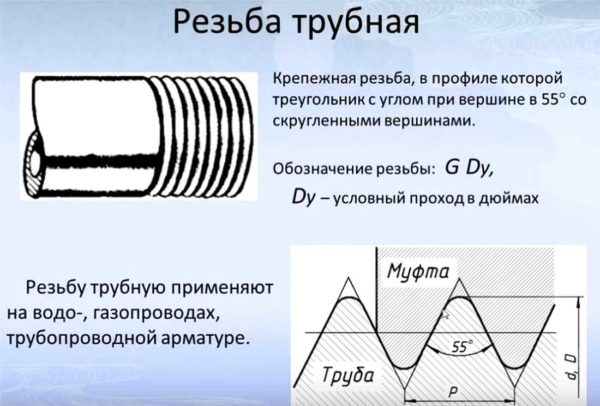
How is pipe thread indicated in the drawings? The letter G and numbers. Number - nominal diameter of the pipe
Cylindrical pipe thread: features, designation, dimensions
Cylindrical pipe threads are described in GOST 6357-81. It is applied to the outside or inside of the pipe. The standard also allows the connection of an outer conical and an inner cylindrical. In general, the thread should be made with roundings, the radius of which is also prescribed. However, for the connection of cylindrical parts, a straight cut of the vertices of the triangle is allowed (but not for connection with a tapered thread).
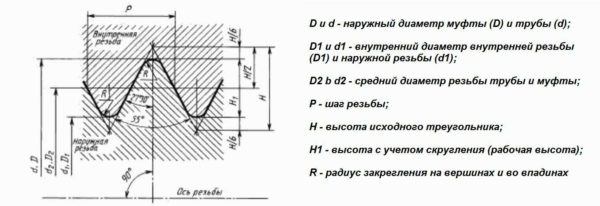
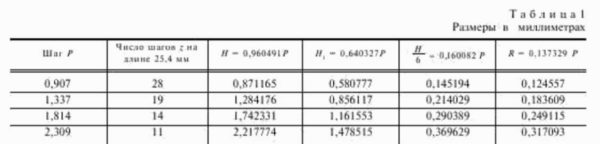
Further dimensions. Cylindrical pipe threads can be external and internal. They are characterized by three diameters: outer, inner and middle. And also the working height of the profile, rounding diameter and pitch. Diameters and number of turns are given in the table.
| Thread size in inches | Step of turns, mm | Number of turns per inch, pcs | Cylindrical pipe thread diameter, mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Row 1 | Row 2 | D = d | D1 = d1 | D2 = d2 | ||
| 1/16 " | 0,907 | 28 | 7,723 | 7,142 | 6,561 | |
| 1/8" | 9.728 | 9.147 | 8,566 | |||
| 1/4" | 1,337 | 19 | 13,15 | 12,301 | 11,445 | |
| 3/8" | 16,662 | 15,806 | 14,950 | |||
| 1/2" | 1,814 | 14 | 20,955 | 19,793 | 18,631 | |
| 3/4" | 22,911 | 21,749 | 20,587 | |||
| 5/8" | 26,441 | 25,279 | 24,117 | |||
| 7/8" | 30,201 | 29,039 | 27,877 | |||
| 1" | 2,309 | 11 | 33,249 | 31,770 | 30,291 | |
| 1 1/8" | 37,897 | 36,418 | 34,939 | |||
| 1 1/4" | 41,910 | 40,431 | 38,952 | |||
| 1 3/8" | 44,323 | 42,844 | 41,365 | |||
| 1 1/2 | 47,803 | 46,324 | 44,845 | |||
| 1 3/4" | 53,746 | 52,267 | 50,788 | |||
| 2" | 59,614 | 58,135 | 56,656 | |||
| 2 1/4" | 65,710 | 64,231 | 62,752 | |||
| 2 1/2" | 75,184 | 73,705 | 72,226 | |||
| 2 3/4" | 81,534 | 80,055 | 78,576 | |||
| 3" | 87,884 | 85,405 | 84,926 | |||
| 3 1/4" | 93,980 | 92,501 | 91,022 | |||
| 3 1/2" | 100,330 | 98,851 | 97,372 | |||
| 3 3/4" | 106.680 | 105,201 | 103,722 | |||
| 4" | 113.030 | 111.551 | 110.072 | |||
| 4 1/2" | 125,730 | 124,251 | 122,772 | |||
| 5" | 138,430 | 136,951 | 135,472 | |||
| 5 1/2" | 151,130 | 149,561 | 148,172 | |||
| 6" | 163,830 | 162,351 | 160,872 | |||
According to the table, there shouldn't be any questions. It is only worth mentioning that if there is a choice, it is worth choosing sizes from row 1. The thread pitch and the number of turns are the same for several pipe diameters. The missing parameters - the working height of the profile and the rounding diameters, are taken from the second table.
A cylindrical pipe thread is designated by the Latin letter G, followed by the nominal diameter of the pipe in inches. For example: G 1/2 ″, G 2 ″, etc. Further it is indicated:
- If the thread is left-handed, the letters LH are put down, if the right-hand thread is empty.
- Accuracy class - A or B (A has less permissible deviations) are hyphenated. For example, G 1 1/8 ″ - A or G 2 ″ LH - B. The second is a left hand thread with accuracy class B.
- Then the make-up length is prescribed (the length of the section in millimeters to which the thread is applied). G 5/8 ″ - A - 40.
If a connection is described - pipe / coupling, for example - the accuracy class is indicated for both parts. For example, G 2 3/4 ″ - A / A or G 1 ″ - B / A. First, the accuracy class of the pipe thread is indicated, then the coupling or the device to be installed.
Tapered pipe thread: features, size table, designation
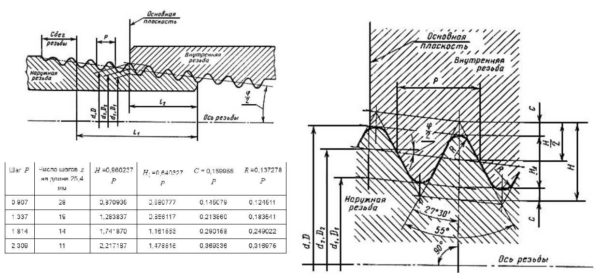
This type of threaded connection is used where high reliability of the connection is required. Tapered pipe threads differ in that they are applied to the cone.In this case, its profile remains exactly the same, but two values are added - the working length of the thread l1 and l2 - the length from the end to the main plane. These columns are added to the table.
| Thread size in inches | Pitch P, mm | Number of turns per inch, pcs | Pipe tapered thread diameter, mm | Thread length, mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D = d | D1 = d1 | D2 = d2 | l1 | l2 | |||
| 1/16 " | 0,907 | 28 | 7,723 | 7,142 | 6,561 | 6,5 | 4,0 |
| 1/8" | 9.728 | 9.147 | 8,566 | ||||
| 1/4" | 1,337 | 19 | 13,15 | 12,301 | 11,445 | 9,7 | 6,0 |
| 3/8" | 16,662 | 15,806 | 14,950 | 10,1 | 6,4 | ||
| 1/2" | 1,814 | 14 | 20,955 | 19,793 | 18,631 | 13,2 | 8,2 |
| 3/4" | 26.441 | 25.279 | 24.117 | 14.5 | 9.5 | ||
| 1" | 2,309 | 11 | 33,249 | 31,770 | 30,291 | 16.8 | 10.4 |
| 1 1/4" | 41,910 | 40,431 | 38,952 | 19.1 | 12.7 | ||
| 1 1/2" | 47,803 | 46,324 | 44,845 | 19.1 | 12.7 | ||
| 2" | 59,614 | 58,135 | 56,656 | 23.4 | 15.9 | ||
| 2 1/2" | 75,184 | 73,705 | 72,226 | 26.7 | 17.5 | ||
| 3" | 87,884 | 85,405 | 84,926 | 29.8 | 20.6 | ||
| 3 1/2" | 100,330 | 98,851 | 97,372 | 31.4 | 22.2 | ||
| 4" | 113.030 | 111.551 | 110.072 | 35.8 | 25.4 | ||
| 5" | 138,430 | 136,951 | 135,472 | 40,1 | 28,6 | ||
| 6" | 163,830 | 162,351 | 160,872 | 40,1 | 28,6 | ||
A cylindrical thread is designated by the letter R with indices that indicate the type of surface:
- Just R for male tapered threads.
- Rc - conical inner.
- Rp - cylindrical inner.
After the letters, the conditional pipe size in inches is put, then, if the application is left-sided, add LH. For example, R 3/4, R2 1/2 LH. When describing threaded connections, the designations are written in the form of a fraction. Usually, the numerator is outside, the denominator is inside. For example, Rc / R 3/8.


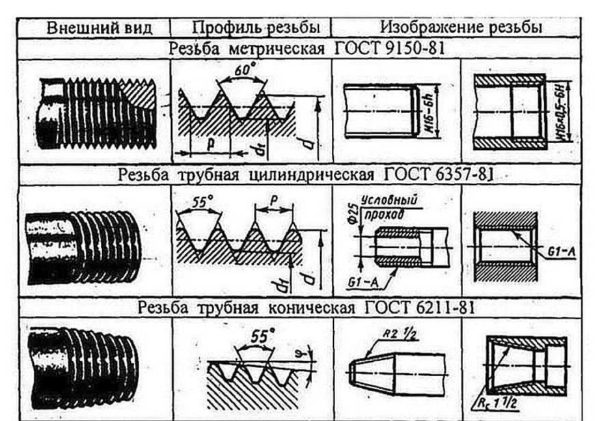
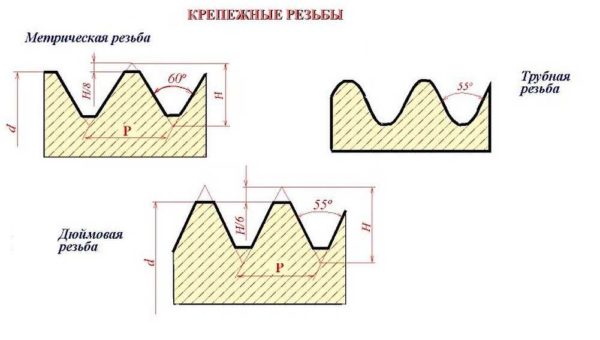
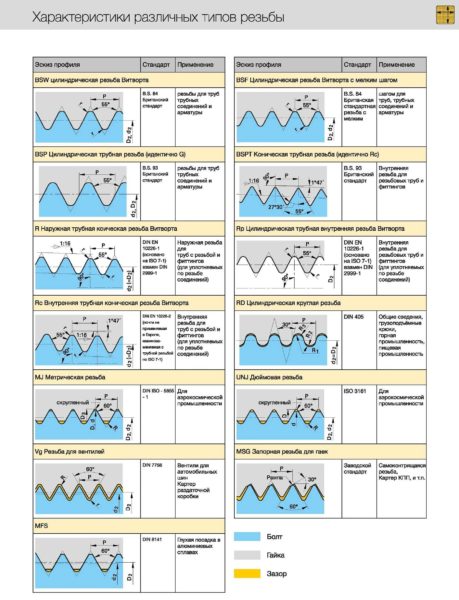










In the pipe thread table, 3/4 "and 5/8" are swapped.
Thank you Yuri! For half an hour I scratched my head while your comment. did not see.