How to look for water on the site
It is very important for home and summer cottages to have water. Some lucky ones can connect to a centralized water supply, but most have to find their own source. How to find water on the site yourself, with your own hands, will be discussed further.
The content of the article
Aquifers and their occurrence
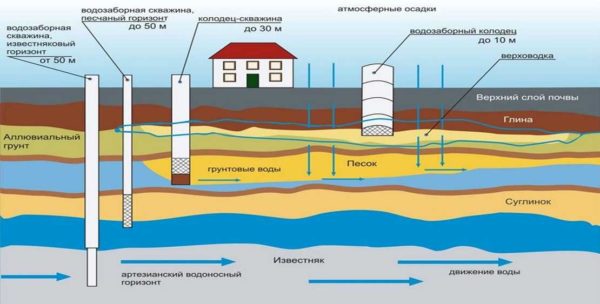
The bedding structure is very heterogeneous. Even in one area at a distance of a meter, the "pie" - the composition of the layers and their sizes - can differ significantly. That is why it can be so difficult to find water on the site; you have to drill several wells to find a normal aquifer. There are three main aquifers:
- Verkhovodka. The depth of such waters is up to 10 meters. The top water is located, as a rule, under the first waterproof layer - clay. In some localities, the top water is already at a depth of 1-1.5 meters, which does not please the owners of such sites - there are many difficulties. Verkhovodka - water, to put it mildly, is not of very high quality - it contains dissolved chemicals from the fields and other pollutants. It can be used for watering, and in order to bring it to a drinking state, a multi-stage purification system.
- Sandy aquifer. Such wells are called "on the sand" and lie at a depth of 30 meters. The water at this level is already cleaner - having passed a multi-layer "filter" of different rocks, it has already been purified. An aquifer sandy layer is usually located under one of the lower located waterproof layers (again, these are clays). The disadvantage of such wells or wells is a large amount of sand in the water, which requires good multi-stage filtration. It is better not to use vibration pumps in such sources - they lift sand.
- Artesian waters. The aquifer at this level is usually limestone. The depth is about 50 meters. The water is always very clean, with a rich mineral composition. The disadvantage is the great depth, therefore, the cost of drilling is high, and the pump is expensive. But artesian wells may not dry out for decades.
I must say that it is not difficult to find a perch on the site. Knowing some of the features of the vegetation, checking some points, you will determine the location of the water carrier with fairly high accuracy.
With an aquifer sandy layer, everything is much more complicated - the depths are serious, you have to focus mainly on the location of wells-wells near neighbors, well, not some indirect signs.
It is possible to find artesian water on the site only with the help of trial drilling. Maps of the occurrence of aquifers can help. Since 2011, in Russia, they are in the public domain (without payment). To get a map of your region, you need to send an application to ROSGEOLFOND. You can do this on their official website, or you can download the forms of the required documents, fill them out and send them by mail (with acknowledgment of receipt).
How to find water on the site using folk methods
There are many popular ways to find water on the site. You can believe in them, you can not believe them, but on average, the percentage of hits is 70-80%, which is not lower than that of "scientific" methods, so it's definitely worth a try.These methods require a certain amount of time and attention, but they are free (if you are looking for water on your site yourself), so it is quite possible to combine them - test several methods, and dig / drill at the point where their readings converged.
Paying attention to plants
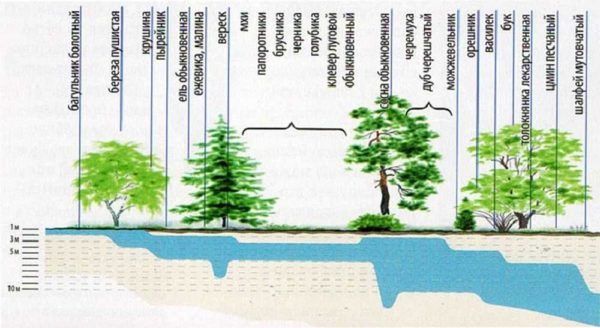
This point makes sense only if the site is not developed, but "populated" with wild plantings. By where and what plants grow, you can quite accurately determine the depth of water.
All that is needed is to walk around the site, see where it grows, put poles near the plants found, on which you can indicate the possible depth of the water. The table contains a list of plants that can be used to determine the presence of water at a particular depth.
| Plant - indicator | The depth of the upper water |
|---|---|
| Cattail, wild rosemary, fluffy birch | 0 - 1 m |
| Sandy reed, buckthorn, wheatgrass, | 1 - 3 m |
| Reed, elk, sarsazan, spruce, blackberry, raspberry, black poplar | up to 5 m |
| Wormwood paniculata, whose brilliant, heather, Scots pine, bird cherry, English oak, | up to 7-8 meters |
| Licorice naked, sandy wormwood, yellow alfalfa (up to 15 m), juniper, hazel, cornflower, medicinal bearberry, beech | 3-5 to 10 meters |
There are several types of trees in the table. We are not talking about massifs, but about single plants, maybe about a small group of plants that "cluster" in one place. In the case of herbaceous plants, the opposite is true - these are not single specimens, but glades occupying a certain area of the soil.
Using frames
On a long-developed area, it will not work to determine by the plants where the water is. Here you will have to apply other methods. One of the most common and highly probable searches is with frames - aluminum wires bent at an angle of 90 °. This method is also called biolocation. Take two pieces of wire 30-40 cm long. A piece 10 cm long is bent at a right angle.
To make the "readings" more accurate, the short pieces are inserted into tubes made from thin branches of an elderberry tree. In the cut branches of the elderberry, the core is taken out, a bent wire is inserted inside. The ends of the wire should move freely.
Taking the frames in both hands, the ends of the wires are spread in opposite directions (180 °) and they walk around the site with them, observing their condition. Somewhere the frames will converge together, somewhere they will turn in one direction (to the right or left - along the flow of water). It is these movements that determine where the water is.
If the frames come together (their ends have moved to some angle), there is water in this place. Going further, you will see that the frames have parted again - the aquifer is over. You can repeat the maneuver from different directions and points, so you can localize the location of the water carrier. If, during the return passage, both frames converge, you have identified the place where you need dig a well or make a well... If the frames have deviated to the right or left, you need to go in that direction and look for a place where they will converge again.
If the frames are stationary, there is no water on the site or the water carriers are located very deep.
Using a vine (wooden slingshot)
You can find water on the site using a wooden slingshot. You need to find two branches that grow from the same point. The branches should be thick, at least 1 cm, even. Try to find them the same thickness. They must be cut off with a piece of the trunk (15-20 cm) on which they grew. You should get a big slingshot.
The leaves are cleaned, the thin ends of the rods are cut, leaving at least 40 cm on each side of the "fork". The branches are bent to the sides so that the angle is at least 150 °, they are fixed in this position and left to dry. The wood may not be completely dry, but the angle should be preserved.
The dried vine is taken by the ends of the fork, held horizontally at shoulder level. In the place where there is water underground, part of the trunk will slope towards the ground. In this place it will be possible dig a well or drill a well. If there are no deviations, there is no water in the area at a shallow depth.
Determination of the amount of water in an underground source
In addition, to find water, it would be nice to also determine its volume. They can be estimated roughly using clay pots and silica gel. They take clay pots, pour silica gel into them, tie the neck with cotton cloth. The packed pots are weighed (the weight can be written on the pot itself). The prepared shells are buried in places where water is supposed to be found and left for a day.
A day later, the pots are dug up and reweighed.
The pot that gained the most weight marks the vein with the most water.
Finding water - watching nature
You can find water on the site simply by observing nature. You have probably noticed that in some places the fog is most dense. Sometimes it even resembles a river - it meanders in some direction. At such points, groundwater is usually the closest. Still need to look at the amount of dew in the morning. If in places where the fog was especially thick, there is more of it, then there is definitely water there.
What else can help find water on the site - watching insects. On a warm calm evening, midges often gather in clouds or pillars. And they are located in certain places. Water sources are usually located under the places of accumulation of insects. If you examine the ground in that place and do not find ant nests, then there really is water there - ants do not make their nests above the water.
How to determine the level of occurrence of groundwater
An approximate estimate of the depth at which the aquifer is located can be by the plants growing above it. As you can see from the table above, certain types of plants do well if the water is not above or below a certain depth. So you can roughly estimate how deep the water is.
For areas where there is a natural reservoir nearby - a river, a lake - you can determine the depth of the water with an accuracy of a meter. For this you need a barometer. With him you go down to the water itself, measure the pressure. Then go to the supposed water source and measure the pressure there. The difference is usually expressed in tenths and every tenth (0.1) is equal to a meter of depth. For example, the difference in measurements is 0.7 mm / Hg. pillar. This means that the water is at a depth of 7 meters.
What else can help find water on the site? Communication with neighbors who already have a well or a well. It is desirable for them to find out where they drilled / dug, how many times, a lot of water or not, at what depth is the water mirror, what quality it is. By the location of all the nearest successful and unsuccessful attempts at neighbors, it is possible, with a fairly high degree of probability, to determine where you have water.