Types and standard sizes of plywood sheets
The oldest sheet building material is plywood. It has been in production for several decades. And, although it is crowded with other more modern materials, it still has its own segment on the market. All this is due to its properties, a large assortment both in size and thickness. What size and thickness of plywood can be, grades and classification, and let's talk today.
The content of the article
Types of plywood and its classification
Plywood is a well-known and popular sheet building material for a long time. It has high flexural strength, both in the longitudinal and transverse directions. In private households, it is used for sheathing frames, flooring. Cheap grades are also used in some construction processes.
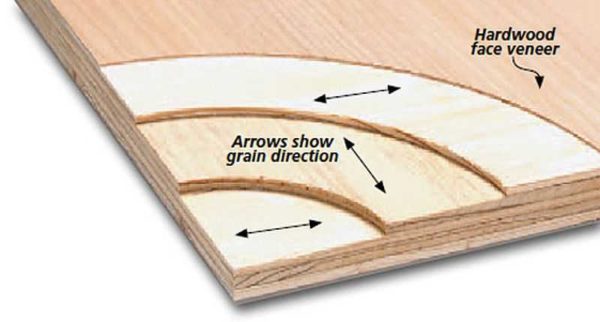
Plywood is made of several veneer layers glued together.
Veneer - wood material, which is thin sheets of wood with a thickness of 0.1 to 10 mm.
The fibers are layered in different directions. This increases the flexural strength of the material in all directions.
Plywood is made from softwood and birch. Birch is more expensive, more often used as furniture. Coniferous is made from all coniferous wood. Cheaper options - from larch, pine and spruce - can be used both for the manufacture of furniture and for construction needs (for example, for frame cladding or for removable formwork in the manufacture of concrete products). They can use Siberian cedar veneer. This type usually comes as a finishing material.
Layers and their number
There are at least three layers in plywood, but maybe more. The layers are arranged so that the veneer fibers are directed in different directions - alternately along the long side of the sheet, then across. An odd number of veneer layers is more common. In private housing construction, three and five-layer plywood is most often used. In this case, the orientation of the layers is selected relative to the central layer.
If on the outer layer the veneer fibers are directed along the long side, the plywood is called longitudinal. It has great flexibility. If the veneer fibers are located along the short side of the sheet, plywood is called transverse and is used where high bending stiffness is required.
Moisture resistance
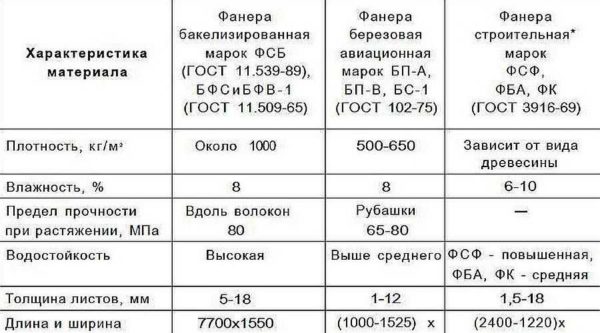
Since glue is used in the manufacture, the entire material has a fairly high degree of water resistance. There are several popular brands of plywood:
- Moisture resistant marked with FC. For its gluing, a glue based on carbamide-formaldehyde resin is used. That is, there is formaldehyde emission. With an emission class E1 and below, it can be used indoors or for the manufacture of furniture.
- Plywood of increased moisture resistance - FSF. The same glue is used only with water-repellent additives. Can be used for outdoor use.
- FSF-TV. The same water-repellent plywood but with flame retardant additives.
- Laminated - practically insensitive to moisture.
If you are looking for material for indoor use and do not want to worry about formaldehyde in the air, look for the FBA brand. It is environmentally friendly, but only suitable for rooms with normal humidity. The FB brand does not swell even under water, there is also BS aviation plywood. She still does not react to chemical environments. It was used in the construction of ships and airliners.
Surface finish
The outer layers of plywood can be sanded during production. There are such types:
- Unpolished. No surface treatment. Marked with NSh.
- Only one side is sanded to smoothness. Sh1 is added to the marking.
- Both sides are sanded - Ш2.
Plywood sanded on both sides is used for the manufacture of furniture. For construction sites, both smooth sides are rarely needed. Usually, if polished is used, then Ш1. And then, if this material is used for decorative cladding. More often at a construction site, an unpolished one is needed - it provides better adhesion to other materials.
Varieties and labeling
There are five grades of plywood. The highest is E (Elite), and further, as it deteriorates, from I to IV. The grade is determined by the state of the upper - front layers. Moreover, the quality of both surfaces is assessed separately and written through a slash (slash). For example, I / II or III / IV.
In GOST, it is described in detail for which grade which surface errors are permissible, there are special tables by which this grade is determined. If at least one parameter is worse than the permissible value, the grade is reduced.
These are the features on the front surface of different grades of plywood.
- Elite. For this brand of plywood, the veneer must be perfect. There can be only minor changes in the wood (no eyes). All. There shouldn't be any other drawbacks.
- I grade... May be
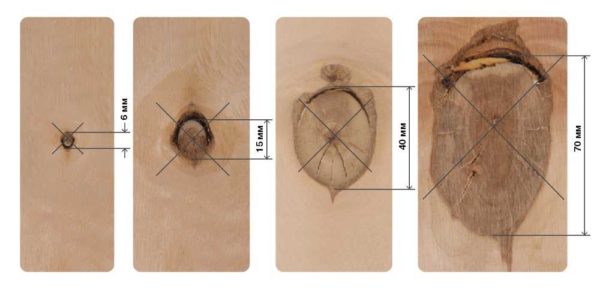
- Knots:
- pin, no more than 3 pcs per square meter;
- healthy, intergrown, dark and light with a diameter of 15 mm, no more than 10 pcs / m², they may have cracks no more than 0.5 mm wide;
- partially accreted, not accrete, falling out with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in an amount of no more than 3 pcs / m²;
- Closed cracks no more than 200 mm long and no more than 1 mm of the sheet width.
- Healthy discoloration - no more than 5% of the area.
- Knots:
- II grade... Allowed:
- Knots:
- pin without restrictions;
- healthy, intergrown, dark and light with a diameter of 25 mm, no more than 5 pcs / m², they can have cracks no more than 0.5 mm wide;
- partially accreted, not accrete, falling out with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in an amount of no more than 6 pcs / m²;
- Closed cracks no more than 200 mm long and no more than 1 mm of the sheet width.
- Open cracks no more than 200 mm long, no more than 2 mm wide, in an amount of no more than 2 pcs when covering with putty.
- Healthy discoloration is allowed.
- The overlap in the outer layers is not more than 100 mm in length in the amount of not more than 1 piece per 1 m of the sheet.
- Leakage of glue no more than 2% of the sheet area.
- Torn fibers no more than 5% of the sheet area.
- Scratches, dents are allowed in depth (height) within the limits of the maximum deviations in thickness.
- The gap in joints with a width of not more than 1 mm is not more than 1 piece per sheet.
- Wood inserts no more than 8 pcs per 1 m².
- Double insert - no more than 2 pcs per m².
- Knots:
- III grade.
- Knots:
- pin without restrictions;
- healthy, fused, dark and light with cracks no more than 1.5 mm wide;
- partially accreted, not accreted, falling out with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in an amount of no more than 10 pcs / m²;
- Close cracks without limits.
- Open cracks
- length no more than 300 mm no more than 2 pieces,
- no more than 600 mm long, no more than 5 mm wide in an amount of no more than 2 pieces when covering with putty;
- Healthy discoloration is allowed.
- The overlap in the outer layers is no more than 200 mm in length, no more than 2 pcs per 1 m of the sheet.
- Leakage of glue no more than 2% of the sheet area.
- Torn fibers no more than 15% of the sheet area.
- Scratches, dents are allowed in depth (height) within the limits of the maximum deviations in thickness.
- The gap in joints with a width of not more than 2 mm is not more than 1 piece per meter of sheet.
- Wood inserts and double insert - unlimited.
- Non-ferrous metal brackets are allowed.
- Knots:
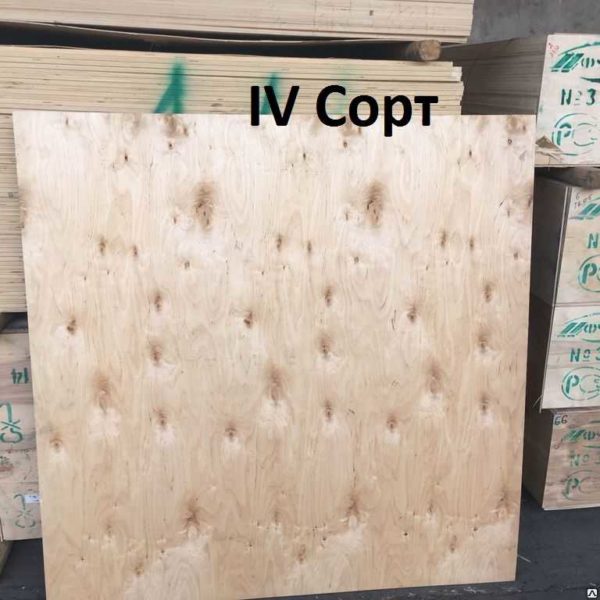
- IV grade may have such defects.
- Knots:
- pin;
- healthy, fused, dark and light without limits;
- partially accreted, not accreted, falling out with a diameter of no more than 40 mm without restrictions;
- Close cracks without limits.
- Open cracks
- no more than 300 mm in length without restrictions;
- no more than 600 mm long and no more than 10 mm wide without restrictions;
- Healthy discoloration is allowed.
- Overlap in outer layers is allowed.
- Leakage of glue is allowed.
- Torn fibers are allowed.
- Joint clearance is allowed.
- Scratches, dents are allowed.
- Wood inserts and double insert - unlimited.
- Non-ferrous metal brackets are allowed.
- Knots:
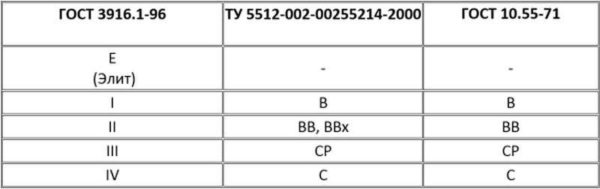
Compliance with the designations of plywood grades according to various standards: GOST 3916.1-96, TU 5512-002-00255214-2000, GOST 10.55-71
If there are defects not listed in the GOST, the product is considered off-grade. It is also considered off-grade when the maximum permissible size of defects is exceeded. Sometimes they try to sell such products as the fourth grade, but this is a re-grading and the price for it should be much lower.
By the way, if there are no obvious cracks and fallen knots, the third grade can be used for interior decoration. In certain interiors, it looks even more interesting than E or the first, which are simply a flat sheet without any peculiarities inherent in wood.
Plywood: sheet dimensions, thickness
Sheet material of various sizes may be more convenient for different jobs. And plywood is no exception. It is produced in different sizes, which are usually divided into standard and not. Standard ones are spelled out in GOST (GOST 3916.1-96), non-standard ones are produced on order - for large companies or those formats that are more in demand in retail. Usually a plywood sheet looks like a rectangle, but it can also be in the form of a square.
Standard plywood sizes
In general, different types of plywood are described by different GOSTs (GOST 2707, GOST 20907, GOST 102-75, GOST 3916.1-96) and they contain different mesh sizes.
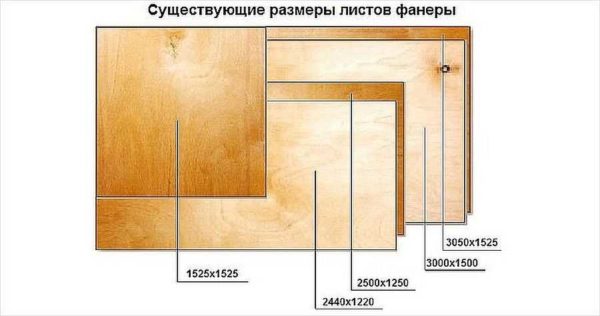
The most common small-format plywood sheets have the following standard sizes:
- 1220 * 1220 mm;
- 1525 * 1220 mm;
- 1525 * 1525 mm.
Small sheets of plywood are good because you can work with them without helpers. But a large number of seams is not good.
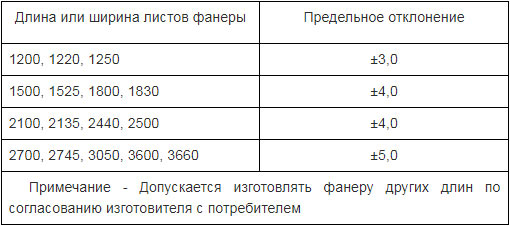
According to GOST 3916.1-96, it is allowed to produce plywood of non-standard length by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
In theory, combinations from the above list can be any. In practice, there are much fewer of them.
Large format
In some cases, it is more convenient to use large-sized plywood sheets - the joints become much smaller. The most commonly used large-format plywood of the following sizes:
- 1830 * 1525 mm;
- 3050 * 1525 mm
- 3000 * 1500mm;
- 2500 * 1250 mm;
- 2440 * 1220 mm.
No one has brought order to the standards, so theoretically you can find almost any size from those that fit into one of them. So, for example, according to GOST 102-75:
- The length of the plywood sheet can be from 1000 mm to 1525 mm. The length increment is 25 mm.
- The width can be from 800 mm to 1525 mm with the same gradation step - 25 mm.
Moreover, the maximum deviation in length and width is 4 mm. The thickness of plywood can be from 1 mm, but this is a rare "aviation" grade. Plain comes in thicknesses from 3 mm to 30 mm, but can be found up to 40 mm. The permissible error in dimensions in thickness is 0.5 mm.
If you study the later standard 3916.1-96, it indicates a different grid of plywood sizes with a specific listing of possible values (see table above).
Thickness
With the thickness of plywood, the picture is about the same: if you wish, you can find from 1 mm to 40 mm thick. The possibility is not excluded that there are thicker options. But most often there are slabs with a thickness of 6 mm to 27 mm.
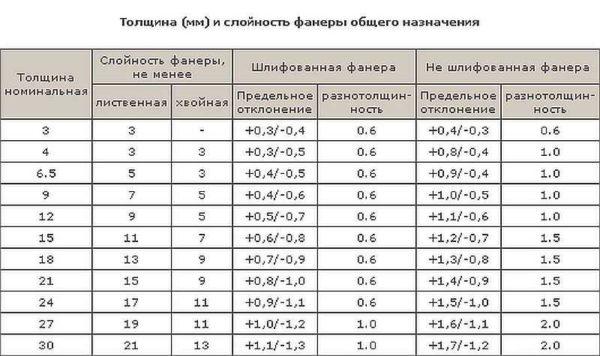
Thickness of hardwood and coniferous plywood, layering and permissible deviations for sanded and non-sanded boards
By the way, it is interesting that in any of the standards the maximum permissible deviation is prescribed - 0.5 mm. Which, taking into account the not always large figure, is not so small. And this deviation can significantly complicate the installation of the material on the floor. The difference has to be corrected with thin pads, or, if it is small, grind off at the joints with a grinder.