Clay ceramic brick - types and dimensions according to the standard
Ceramic bricks are one of the oldest materials for building houses. Over time, the technology has hardly changed. To improve the thermal characteristics, they came up with the idea of making voids. To reduce construction time, they began to produce large products. The assortment has increased. One size of ceramic bricks is clearly not enough for modern construction. But the essence of the production and the materials used remained the same. As well as problems.
The content of the article
Pros and cons of ceramic bricks
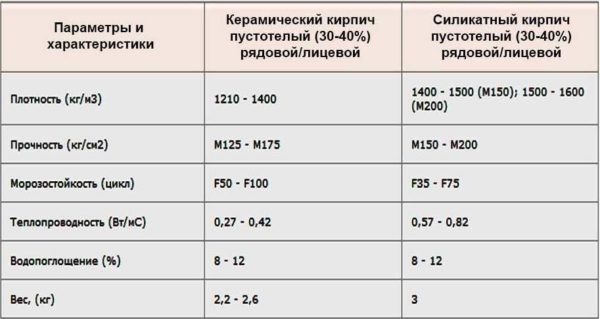
The advantages of ceramics include naturalness, harmlessness. If we compare ceramics and silicate, then clay products slightly benefit from thermal conductivity. If you look at the indicators, then the difference is very small. But a ceramic house is much warmer than a silicate one. The point is the higher heat capacity. Clay can store more heat and is therefore warmer at home.
Ceramics is inferior to silicate in sound insulation properties, as well as in geometry and stability of characteristics. This is its main disadvantage. Moreover, at a high price, there are often efflorescences, with which it is very, very difficult to fight. Another drawback is that even the front surface is rarely even.

Ceramic brick is a traditional material for building houses, which is more than one hundred years old
All these shortcomings are understandable. Ceramic bricks are obtained by firing pre-formed parallelepipeds from clay mortar. Clay is a natural material that has various properties. The different properties of different types of clay are the main reason that the size of ceramic bricks does not differ in stability. Moreover, a significant spread can be within the same batch. And from party to party, in general, there may be significant differences. The different characteristics of the feedstock also cause a wide variation in the characteristics of the finished product. Such as strength and density.
Service life - reality is not happy
In many respects, ceramics should be better than the same silicate, but the reality is different. Recently, too often red ceramic bricks are found crumbling, dilapidated after several years of operation under normal conditions. The reasons are the complexity of the technology. For a good result, careful processing and preparation of the clay is required in order to exclude lime inclusions, which are the reasons for "shooting". And this is additional time in an already not short production cycle. And extra energy. And expensive equipment, which is not bought by everyone.
The second point: holding the temperature regime of firing. Burnt ceramic bricks behave normally in masonry. It looks only worse, as it is darker than the "norm". It's not so scary. But the unburned one collapses, crumbles. And that makes him dangerous. Ceramics are fired in the furnace for a long time, and so it takes a little to reduce the time in order to increase productivity. Hence the underburning. Or fuel economy, which is far from cheap. So compliance with the technology for the production of ceramic bricks is a high price of products. And expensive bricks are bought very reluctantly. So the collapsed red brick most likely had a low price. And everyone knows that cheap is very rare.Nevertheless, the budget for a construction site is usually not rubber and you have to save.
No matter how complex the production technology is, European supplies have a geometry close to ideal, standard dimensions and stable quality. Their price is far from budget, but quality problems are rare. So if the funds allow, they try to buy imported bricks. Domestic clay, even expensive, still cannot boast of stability of quality. That is why, although ceramics should be better in many respects, more and more often the choice is made in favor of silicate. Because for quite reasonable money you can buy good quality building material. He is chosen even though he is much colder. All the same, to achieve the required level of energy efficiency, it is necessary to insulate the ceramics too.
Types and size of ceramic bricks according to GOST 530-2012
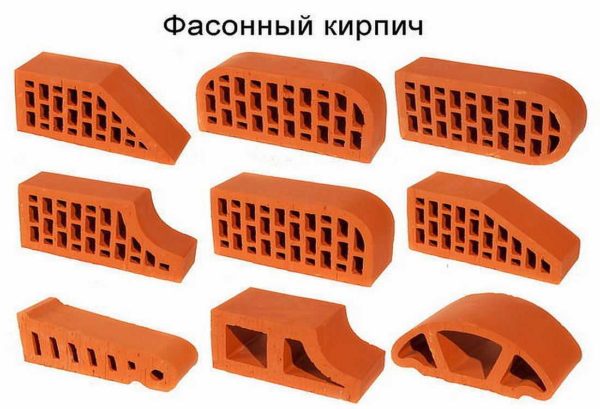
In terms of size, ceramic products are divided into brick and stone. Ceramic building stone differs only in its greater thickness - not less than 140 mm. Clay brick can be solid and hollow, ordinary (building) or finishing (front). Ceramic stone - only ordinary and only hollow. Voids in clay stone or brick can be located both parallel to the bed (the working surface on which the mortar is placed) and perpendicularly. In addition, the standard defines the following types of products:
- Shaped brick. A product that differs in shape from a parallelepiped.
- Complementary element. The form is specially designed to complete the laying.
- With tongue-and-groove system. Ceramic stone, the vertical edges of which are specially shaped for joining without mortar. The sizes of the protrusions are not standardized. There are two special sizes for this type of material:
- Working width of the stone. This dimension does not include the tongue-and-groove protrusions. It forms the width of the masonry.
- Out of service stone length. The distance from one vertical surface to another, taking into account the protrusions.
Also, stone and brick can be with a polished or unpolished bed (this is the part on which the mortar is placed). Some factories produce material with a notched spoon. This type is convenient to use if the wall will be plastered. Notches are needed for better adhesion to the plaster.
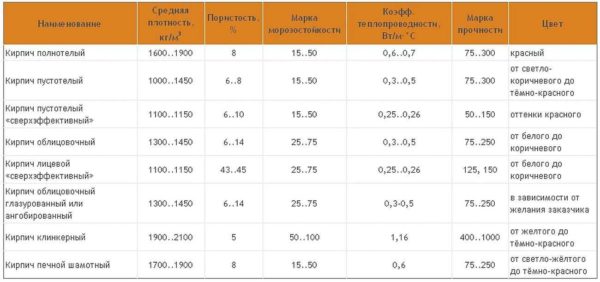
There is also clinker brick. It has a more complex manufacturing technology, which gives it special properties. It is stronger than usual construction material and has a lower water absorption. Its surface is perfectly flat and smooth, which makes it possible to use it as a finishing material. But this is a separate group of products.
Standard sizes and designation of ceramic building (ordinary) bricks
According to the GOST 530-2012 standard, there are the following sizes of ceramic bricks:
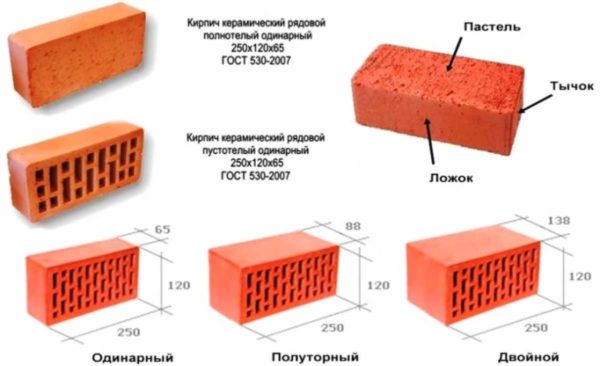
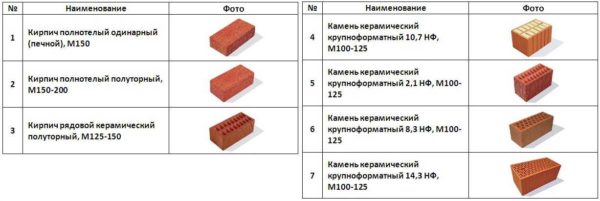
- Normal or single... They put in the markingNF... It hasdimensions 250 * 120 * 65 mm... According to the previous standard (GOST 530-2007), this brick size was called single. If this is material for masonry walls, put KR (private). Can be full-bodied or with vertical voids. According to the same standard, there are its subspecies:
- 0.5 NF - 250 * 60 * 65 mm.
- 0.7 NF - 250 * 85 * 65 mm.
- 0.8 NF - 250 * 120 * 55 mm.
- 1.3 NF - 288 * 138 * 65 mm. This is an oversized size.
- 1.4 NF - 250 * 120 * 88 mm. This is the type that, according to the old standard, is called one and a half.
- 1.8 NF - 288 * 138 * 88 mm. This is the one called double.
- FROM horizontally located voids - designation KRG... There can be only two sizes:
- 1.4 NF - 250 * 120 * 88 mm.
- 1.8 NF - 288 * 138 * 88 mm.
These are the dimensions that are defined for ceramic bricks by the new standard.As for the coefficients, they are calculated as a fraction of the volume occupied by a standard size ceramic brick - 250 * 120 * 65 mm.
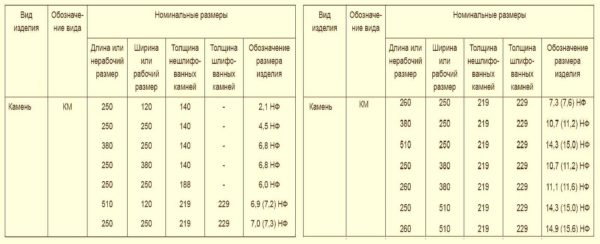
Types and sizes of ceramic stone
As you can see, there are two subspecies of ordinary ceramic (building) bricks, the width of which is 138 mm. At the same time, the standard says that all products with a width of 140 mm or more are called ceramic building stones. So the difference of two millimeters is significant in this case.
The size of the ceramic stone is shown in the tables. The designations of dimensions for products with polished edges are given in brackets. In general, building walls from a large type is much faster, and a square meter of masonry is cheaper. The savings come from the solution. But working alone will not work. One block, even though they are all hollow, can weigh more than ten kilograms. You can install them only together, as well as correct the position. By the way, the standard allows making voids in the lateral faces for grippers (for more convenient transfer) with a total volume of no more than 13%. This really makes it easier to work with large format blocks.
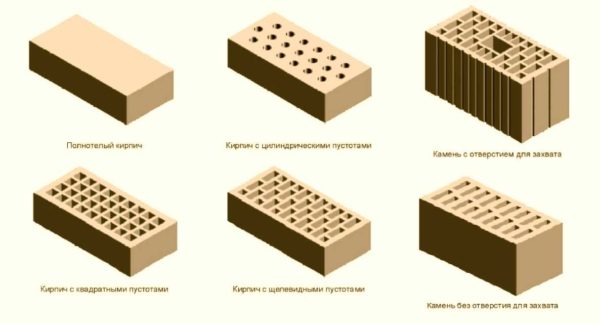
Corpulent and hollow
Solid and hollow ceramic bricks, although produced in the same way, have different purposes. Material without voids goes to load-bearing walls, with voids taken for better thermal insulation characteristics. Since the presence of air pockets makes the material "warmer". It conducts heat worse, which means it saves it better. In the marking, corpulent is indicated by the letters "by", with voids - by the letters "pu". The number of voids and their volume is not indicated anywhere. They should be viewed "locally".
It is necessary to take into account such a feature of the introduced standard. Solid brick GOST 530-2012 is defined as a building material without voids or with voids less than 13%.
In general, solid bricks are used for walls that can be heavily loaded. If the bearing capacity of the masonry is important to you, it is necessary to clarify not only the brand of products in terms of strength, but also the presence of voids. In a solid brick, their size and location are not standardized in any way (if they are less than 13%).
In hollow brick and stone, the diameter of vertical cylindrical voids cannot exceed 20 mm. If the void is square or rectangular, its side also cannot be more than 20 mm. The position and dimensions of the horizontal voids are arbitrary, which is worth remembering. Only the minimum outer wall thickness has been determined. It should not be less than 12 mm for brick and 8 mm for stone.
Specifications
The standard defines strength grades, frost resistance and density class. Strength grades represent the load that a material can bear. It is easy to decipher this value. The number that follows the letter "M" is the number of kilograms per square centimeter that the material can withstand without destruction. Example: M150 means that ceramic bricks of this batch will withstand a load of 150 kg / cm².
| Strength grades | Ceramic bricks | M100, M125, M150, M175, M200, M250, M300 |
| Ceramic stone | M300, M400, M500, M600, M800, M1000 | |
| Clinker bricks | M25, M35, M50, M75, M100, M125, M150, M175, M200, M250, M300; | |
| Brick and stone with horizontal voids | M25, M35, M50, M75, M100 | |
| Frost resistance | F25, F35, F50, F75, F100, F200, F300. | |
Frost resistance is indicated by the letter F and a number. The figure represents the number of freeze / thaw cycles that do not change characteristics or appearance. For example, F50 - 50 freeze and thaw cycles. For internal partitions in heated buildings, frost resistance can be taken low - a positive temperature will still be maintained.
Thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal resistance
The density class corresponds to the average density of the material, but the energy efficiency of the material also depends on the density. The lower the density, the better the thermal insulation properties. But it will not be possible to significantly reduce the density for external walls. They must carry a certain level of load. Therefore, in recent years, a brick house has been made with insulation.
How to work with the last two tables? The density class is indicated in the marking. By this characteristic, you can find out the mass of a ceramic brick cube. It is listed in the first table. The second table helps to compare the density of the material and the coefficient of thermal conductivity of masonry from it. For example, the density class of ceramic bricks is specified as 1.0. This means that the cube should weigh 810-1000 kg, and the masonry on a minimum layer of glue after drying will have a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.20-0.24 W / (m * ° C).
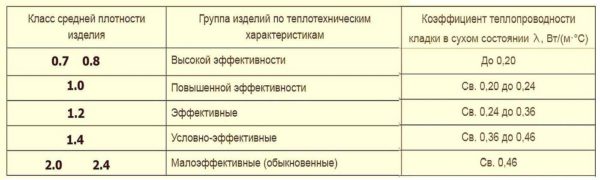
Groups of ceramic bricks and blocks according to the thermal characteristics of masonry (with a minimum amount of mortar)
It is worth saying that according to modern standards, none of the types of bricks gives the necessary thermal resistance. Unless the thickness of the wall will be more than a meter.

Masonry of ceramic bricks of one and a half or two bricks does not meet modern requirements for thermal conductivity of external walls
In this case, a hollow brick or a ceramic building block wins, since they have the best thermal conductivity characteristics. The wall will be a couple of tens of centimeters already - not 147 cm, for example, but only 105. So, in any case, it is worth considering additional insulation of the outer walls.
Ceramic brick weight
The weight of ceramic bricks depends on the density and the presence / number of voids. The exact figure is recognized in the accompanying documents, and then, the spread within one batch is up to 10%.
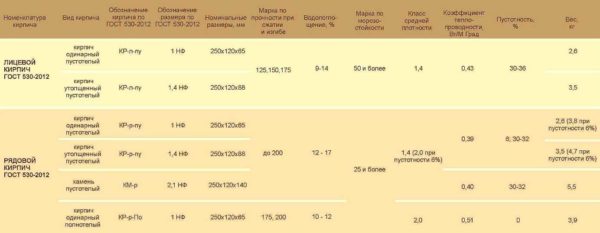
The characteristics indicate the weight of different types of bricks: masonry, finishing, with and without voids
Using the old terminology, the approximate weight of ceramic bricks will be as follows:
- Single (type 1 NF, size 250 * 120 * 65 mm):
- corpulent (private, masonry, construction) 3.3-3.6 kg / piece;
- worker (private, masonry) hollow - 2.3-2.5 kg / piece;
- facing (front, finishing) hollow - 1.32-1.6 kg / pc.
- One and a half has a mass (type 1.4 NF, dimensions 250 * 120 * 88 mm):
- full-bodied private - 4.0-4.3 kg / piece;
- hollow private - 3.0-3.3 kg / piece;
- facial hollow - 2.7-3.2 kg / pc.
- Double weighs (1.8 NF 288 * 138 * 88 mm.):
- ordinary corpulent - 6.6-7.2 kg / piece;
- ordinary hollow - 4.6-5.0 kg / pc.
We give an approximate weight, since the density and number of voids for each plant can differ significantly. The number of voids is not regulated, so the finishing materials can be lightweight.
Ceramic brick marking
In the marking of ceramic bricks, complete information about its type is indicated. The size of the brick is indicated in millimeters in the format: length * width * height. The main characteristics given above must be indicated. To decipher the information, one must remember the conventions of each type of material:
- K - brick
- Cl - clinker.
- P - private (construction).
- L - front (finishing, decorative).
- Г - horizontal voids.
- Po - corpulent.
- Pu is empty.
- Ш - polished.
- PG - tongue-and-groove.
After specifying the dimensions, through the oblique there is an indication of the strength class, average density class and frost resistance. Here are some examples of marking and its decoding:
- KR-r-on 250 * 120 * 65 / 1NF / 200 / 2.0 / 50. You need to read it like this: ceramic brick (KR), ordinary (p), corpulent (by). Dimensions 250 * 120 * 65 mm, 1NF - format and dimensions. Then there are: strength class M 200, average density class 2.0, which corresponds to 1410-2000 kg / m³, frost resistance F50 (50 cycles).
- KRG-l 250 * 120 * 88 / 1.4NF / 50 / 1.2 / 75.It sounds like this: ceramic brick (KR), with horizontal voids (G), front (l). The size of the ceramic brick is 250 * 120 * 88 mm, the standard size is 1.4 NF. Strength class M50, average density class 1.2, which corresponds to a weight of 1010-1200 kg / m³. Frost resistance 75 cycles (F75).
- KM-pg 510 / 10.7NF / 150 / 0.8 / 75. This designation is deciphered as follows: a ceramic stone (KM) with a tongue-and-groove connection (PG), the size of the working part is 510 mm, standard size is 10.7 NF. Strength grade M150, density class 0.8 (energy efficient), frost resistance F 75.
The new labeling method is close to EU standards. The standard does not prohibit factories from specifying additional characteristics in the accompanying documents. You can also add additional information to the package, which makes it easier to identify the manufacturer.