Lightweight concrete in private construction
Saving energy is becoming a necessity, and one of the main costs in our climate is heating. In this regard, new materials are being developed that allow you to build warm houses and insulate existing ones. Lightweight concrete is becoming more and more popular. This is a whole group of materials with a fairly wide range of properties and characteristics.
The content of the article
Types of lightweight concrete
The reduction in concrete mass occurs due to the formation of pores and the use of lightweight aggregates instead of traditional gravel, and sometimes sand. Sometimes, pores are formed by various processes. Depending on the method of production, lightweight concretes are divided into three groups:
- Aerated or porous concrete. It is obtained by a mixture of a binder, water, sand (in some brands there is no sand) and additives that form a foam or promote gas formation. When using foam, foam concrete is obtained, when using gas-forming additives, aerated concrete. If aerated concrete most of the binder is lime, a gas silicate is obtained. The main difference between cellular materials is the absence of large aggregate.
- Ordinary lightweight concrete. Received from a mixture of binder, coarse and fine aggregate, water. They differ from ordinary concrete by the presence of light porous aggregate instead of crushed stone. Almost all the voids between the filler particles are filled, there are few air cavities in such a material - no more than 6%.
- Coarse-porous lightweight concrete. Instead of sand and gravel, a coarse porous aggregate is used, which is mixed with a binder diluted with water. There is no sand, because this material is also called sandless concrete. Fragments of filler stick together only in those places where they touch, leaving the voids unfilled. Air voids can be up to 25%.
But in each of the groups there can be many varieties and compositions. Different aggregates and binders are used. Traditionally, cements are used as a binder (on Portland cement, materials have better strength characteristics). The second most popular binder is lime, less often gypsum is used. Sometimes they can use a mixture of binders and use water glass.
Hardening technology
There are three technologies for the manufacture of aerated concrete:
- Natural hardening. The composition poured into the forms is left indefinitely in the formwork. After a certain time (depending on the composition and type), the formwork is removed. Using this technology, the material is the cheapest, but its characteristics are in the lowest part of the permissible range, and sometimes even lower.
- Processing in heat and heat humidity chambers at atmospheric pressure. The quality indicators are higher, but also the costs and the price are higher.
- Autoclave hardening. The material acquires excellent characteristics, but it is also more expensive due to expensive equipment and energy costs (to maintain the temperature and pressure in the chamber).
Placeholders
By origin, aggregates for lightweight concrete can be divided into two groups: natural (natural) and artificial.Natural ones are obtained by grinding natural porous materials: shell rock, pumice stone, lava, turf, limestone, etc. The best of them are pumice and volcanic turf. They have a closed pore structure, which reduces the amount of moisture absorbed by the material.
Artificial aggregates for lightweight concrete are wastes from some technological processes (slags) or materials specially created from natural components (expanded clay, vermiculite, perlite, etc.), as well as some chemical aggregates (polystyrene).
Properties, characteristics, application
The main characteristics of lightweight concrete that you should pay attention to when choosing are density (bulk density), strength, thermal conductivity and frost resistance.
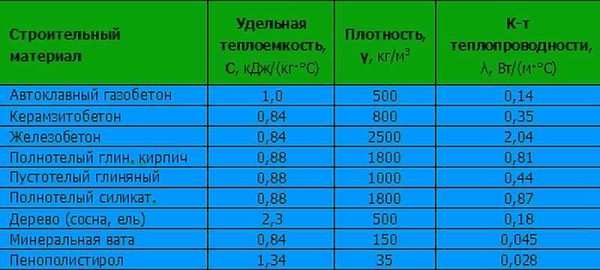
The density of the material depends mainly on the characteristics of the filler, as well as the consumption of binder and water. It can vary widely - from 500 to 1800, but most often it is in the range of 800-1500 kg / m3... The exception is porous or cellular concrete (foam and aerated concrete). Their density can be from 200 kg / m3.
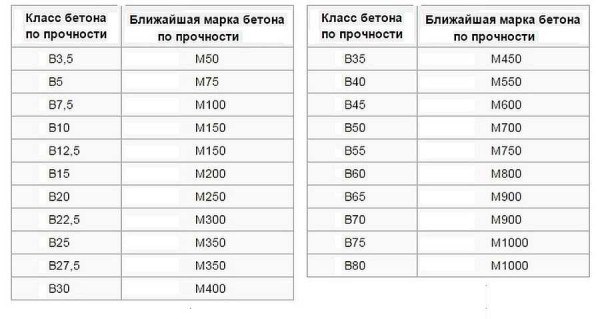
The main operational characteristic is compressive strength. It is subdivided into classes, denoted in the specification by the Latin letter "B", followed by numbers. These numbers displays the pressure that a given material can withstand. For example, the B30 strength class means that in most cases (according to GOST 95%) it can withstand a pressure of 30 MPa. But in the calculations, a safety margin of about 25% is taken. And when calculating for class B30, a strength of 22.5-22.7 MPa is laid.
At the same time, such a characteristic as the compression limit is used. It is denoted by the Latin letter "M", and the following numbers are taken equal to the volumetric mass of concrete in kg / m3.
The thermal conductivity of lightweight concrete is inversely related to density: the more air a material contains, the less heat it conducts. This parameter varies within a significant range from 0.07 to 0.7 W / (mx ° C). The lightest materials with low density are used as thermal insulation. They are used to sheathe the walls of buildings and outbuildings. Warming of balconies and loggias with foam concrete is very popular. But the greatest economic effect can be obtained when building from lightweight concrete of medium density. It has sufficient load-bearing capacity to build a two- or three-storey house. In this case, additional insulation is not required.
Another important characteristic is frost resistance... It is designated by the Latin letter F, after which there are numbers, showing the number of defrost / freeze cycles that a material can endure without losing strength. In cases with lightweight concrete, its frost resistance directly depends on the amount of binder in the composition: the more there is, the more frost-resistant the concrete will be.
Appointment
By purpose, lightweight concrete is divided into the following groups:
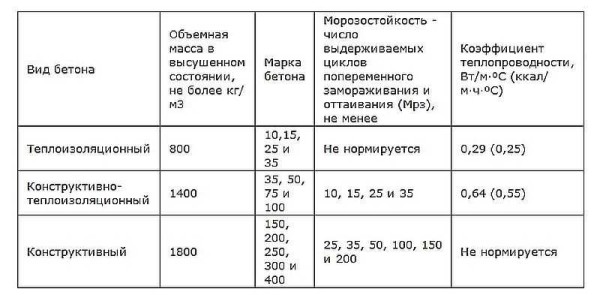
- Heat insulating. Have thermal conductivity not higher than 0.25 W / (mx ° C), density not more than 500 kg / m3.
- Structural and thermal insulation. Thermal conductivity not higher than 0.6 W / (mx ° C), density 500-1400 kg / m3, strength grade not lower than M35. In low-rise private construction, they are used for the construction of load-bearing walls, in multi-storey - for unloaded walls.
- Structural. Density from 1500 kg / m3 and higher, strength grade not less than M 50 and frost resistance not less than F 15. Used for the construction of load-bearing walls for buildings above 3 floors.
Advantages and disadvantages
If we talk about the use of lightweight concrete as insulation, then there are few downsides. The main one is high hygroscopicity, which, nevertheless, varies widely and strongly depends on the filler and the type of material. The second not very pleasant moment is the need to select the appropriate finish. When it comes to outdoor decoration (from the street side), then when choosing materials or type of decoration, it is necessary to take into account the high vapor conductivity. In this regard, either special steam-conducting plasters are used or cladding with a ventilation gap is made.
But the advantages of lightweight concrete as a heater are more significant. It is easy to install, lightweight, easy to cut and saw, tolerates weather changes well, does not require the use of a windscreen. To all this, add high thermal insulation properties and a low price.
If we talk about the use of lightweight concrete as a material for building houses, their advantages are as follows:
- High thermal insulation characteristics. This property allows you to refuse additional wall insulation and reduce the thickness of the walls.
- Light weight. Walls made of lightweight concrete weigh several times less than traditional "heavy" materials and are comparable in weight to the mass of wooden houses. Low weight leads to a "lightening" of the foundation and the possibility of using simpler structures. And this significantly reduces construction costs, as well as transportation costs (they consider, mainly, the delivery of building materials by tonnage).
- The low weight allows the production of large building blocks and slabs, which are nevertheless laid by hand. This leads to a reduction in construction time, as well as a decrease in the number of joints, which in this case are cold bridges.
- Plasticity of the material and ease of processing. Many lightweight concretes are easy to cut, sawn and grind. This allows them to be used for the manufacture of various architectural and decorative elements, as well as to obtain parts of the required size right on site by sawing the existing blocks into smaller fragments.
- They tolerate changes in operating conditions well. Changes in humidity and temperatures have practically no effect on the material. They also hold constant loads well, and are not particularly sensitive to mechanical stress. Dents appear in the material, but the integrity of the block is difficult to break.
- Waste products are often used as aggregates. This reduces the cost of the material while reducing the environmental burden.
- Some types of lightweight concrete can be made independently (usually with aggregates of slag or expanded clay), reducing construction costs to a minimum.
As you can see, lightweight concrete has a lot of advantages as a building material. But not everything is so cloudless. There are disadvantages to be aware of in order to make an informed decision:
- To increase the strength of the walls, frequent reinforcement is necessary. This - additional costs for materials and time for laying reinforcement.
- Insufficient resistance to cracking. The inhomogeneous structure of the material leads to the fact that in the presence of uneven loads (uneven shrinkage of the foundation, for example) cracks appear in the blocks. If they are thin, cobweb-like, they do not affect the strength of the structure, although they look intimidating.
- High moisture absorption. The thermal insulation characteristics of wet materials are significantly reduced. Therefore, during construction, it is important to make high-quality waterproofing. If you plan to use in conditions of high humidity, it is recommended to use pumice, aggloporite and expanded clay as aggregates.
- The low density of materials leads to the fact that fasteners do not hold well in such walls. The material holds vertical loads well, but the “pull-out” is bad. For lightweight and cellular concrete, special fasteners have been developed, but the best solution is to install mortgages in the places where heavy objects are supposed to be fastened.
- The difficulty of choosing an exterior finish. As already mentioned, this is either a cladding with a ventilated facade, or special plasters.
- For interior decoration, a high-quality preliminary primer of the walls may be required - for better adhesion to plaster or putty.
- Low sound absorption.Due to the large number of voids and concrete "paths" passing between them, sounds are transmitted very well. For normal sound insulation, additional materials are required.
Most of the shortcomings, rather, are operational features, but they must be taken into account. Then there will be no unpleasant surprises, and all the features will be taken into account even at the planning stage.
Where and how to use at a construction site, examples of DIY manufacturing
As can be understood from all that has been said, lightweight concrete can be used for any structure. They are used to build walls, use them as insulation, pour slabs for floors, make a screed. But all these tasks require different characteristics. They are "recruited" by the selection of components.
How to choose a recipe
For example, a floor screed needs strength, hydrophobicity and low thermal conductivity. Strength and a decrease in the amount of absorbed moisture gives the use of Portland cement as a binder. Since the best natural additives that provide low moisture absorption - pumice and volcanic turf - cannot be called generally available, expanded clay or polystyrene balls can be used to increase thermal conductivity. They also absorb little moisture.
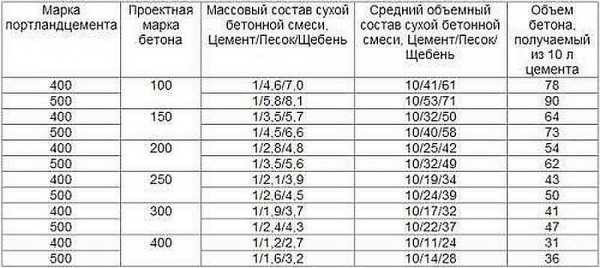
Now about the proportions. They are taken as standard for a given brand. And depending on the type chosen (sandless or regular), the placeholder is replaced. For floor screed, ordinary lightweight concrete is most often used. In them, the gravel is replaced with the selected aggregate, which is added in the required proportion. Only they take less water, making the solution so dense or fluid that it can only be laid.
Even in production, the exact composition of lightweight concrete is determined experimentally each time. This is due to the fact that aggregates have very different characteristics, both in terms of weight and density and other parameters. Several small batches are made with different aggregate compositions (large, small, their proportions, several different types of aggregate are combined) and different amounts of water. After hardening, it is determined which one is best suited for a specific task. Using the same method, you can independently determine how much and what kind of aggregate it is better to pour, and then seal large volumes.
An example of insulating an attic with polystyrene concrete
For an example of experimental selection for specific tasks, see the video. It was required to select a composition for insulating the attic floor. It was decided to use polystyrene concrete as warm and light. A sandless composition was chosen and only polystyrene balls were poured as filler.
According to the selected recipe, lightweight concrete was mixed and the attic was insulated. The process can be seen further.
But this composition is suitable only for insulation in places with a low load. If you need a screed with thermal insulation characteristics on the floor, take a traditional recipe with sand, and replace the filler with polystyrene balls. Reinforcing fibers such as fiber can be added to improve the strength characteristics. To improve plasticity, you can add, as in the video clip, a certain amount of dish detergent or liquid soap. In general, the optimal composition should be determined experimentally.
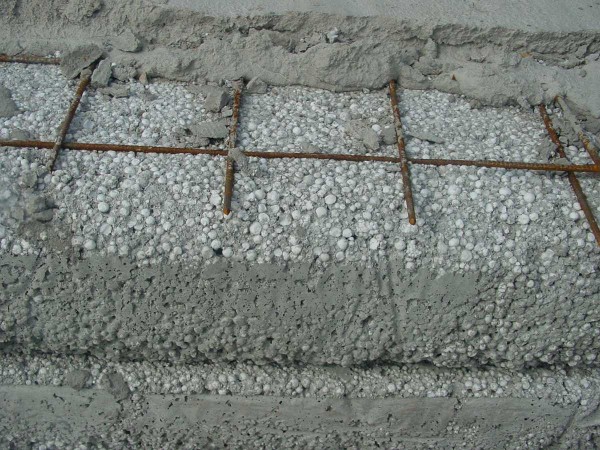
An example of pouring a screed from polystyrene concrete can be seen in the following video. No news, except for a different composition: there is sand. The result is a more uniform structure with cavities filled with concrete and small air bubbles.
What else you need to know is that it is better not to use crumb for the production of polystyrene concrete. For normal characteristics, balls are needed, and not any, but those that will adhere well to the solution.They have a strong film on the surface and do not absorb cement laitance, due to which they have good thermal insulation properties. The crumb obtained by crushing defective slabs has an uneven and torn structure. As a result, it is impregnated with cement milk. Naturally, such concrete will be warmer than usual, but not the same as with granular.
Expanded clay concrete in private housing
Another popular aggregate for the production of lightweight concrete at home is expanded clay. It is made of clay with added substances that increase in volume when heated. This composition is loaded into the furnace, where swelling occurs and followed by firing. But, as studies have shown, many clays give off radiation, as a result, expanded clay also has a background radiation, sometimes even unsafe for health. So you need to be ready for his choice - have a dosimeter.
The selection procedure here is similar to that described above. Only the ability to change the proportions of the large and medium fractions is being added. It is also possible to add or not to sand and obtain results of different structure and characteristics.
Expanded clay concrete is used for pouring into molds and obtaining building blocks, and it is also possible to erect walls with movable formwork. Unlike expanded clay concrete blocks, this technology can be used for the construction of load-bearing walls.
And in this video - the experience of living in a house made of monolithic claydite concrete.
Houses made of sawdust concrete - arbolit
Another natural filler that costs mere pennies and can be used for private housing construction is sawdust, or rather shavings with sawdust. A very small fraction is unsuitable for this material; waste from cylindering of medium or large size is needed.
The composition in this case is sandless, but the proportions are preserved: for 1 part of concrete, 6-7 parts of aggregate are taken. In this case, sawdust. To increase the hydrophobicity of the composition, add liquid glass or calcium chloride.
The second option for mixing and proportions
Here - reviews of residents


















Required lightweight concrete in ready-made bags!