How to choose a cable size
When laying electrical wiring, you need to know which cable section you will need to lay. The choice of the cable cross-section can be done either by the power consumption or by the current consumption. You also need to take into account the length of the cable and the method of installation.
The content of the article
Choosing a cable cross-section by power
You can select the cross-section of the wire according to the power of the devices that will be connected. These devices are called load and the method can also be called "by load". This does not change its essence.
Collecting data
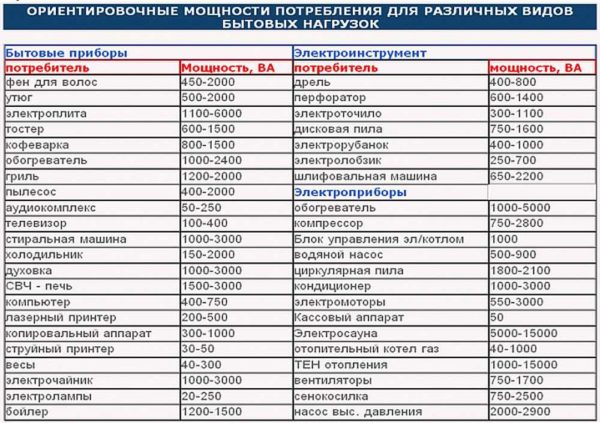
To begin with, find the power consumption in the passport data of household appliances, write it down on a piece of paper. If it's easier, you can look at the nameplates - metal plates or stickers attached to the body of equipment and equipment. There is basic information and, more often than not, power is present. The easiest way to identify it is by units of measurement. If the product is manufactured in Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, the designation W or kW is usually indicated, equipment from Europe, Asia or America usually has the English designation for watts - W, and the power consumption (which is exactly what is needed) is indicated by the abbreviation "TOT" or TOT MAX.
If this source is not available either (the information is lost, for example, or you are just planning to purchase equipment, but have not yet decided on the model), you can take the average data. For convenience, they are summarized in the table.
Find the equipment you plan to install, write out the power. It is sometimes given with a wide spread, so it is sometimes difficult to understand which figure to take. In this case, it is better to take the maximum. As a result, in the calculations, you will have slightly overestimated the power of the equipment and you will need a cable of a larger cross-section. But for calculating the cable size, this is good. Only cables with a smaller cross-section than necessary are burning. Tracks with a large cross-section work for a long time, as they heat up less.
Method essence
To select the cross-section of the wire for the load, add up the power of the devices that will be connected to this conductor. In this case, it is important that all powers are expressed in the same units of measurement - either in watts (W), or in kilowatts (kW). If there are different values, we bring them to a single result. To convert, kilowatts are multiplied by 1000 to get watts. For example, let's convert 1.5 kW to watts. This will be 1.5 kW * 1000 = 1500 W.
If necessary, you can do the reverse conversion - convert watts to kilowatts. For this, we divide the figure in watts by 1000, we get kW. For example, 500 W / 1000 = 0.5 kW.
Further, in fact, the selection of the cable cross-section begins. It's very simple - we use the table.
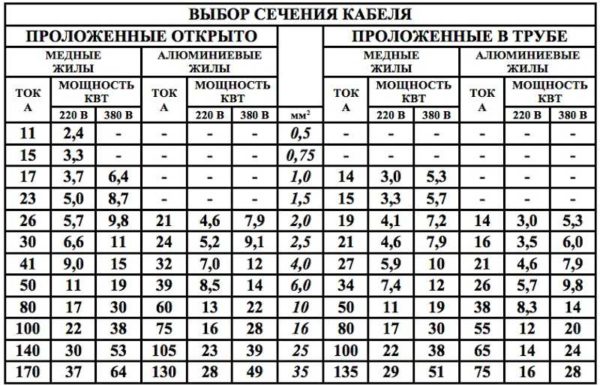
| Cable section, mm2 | Conductor diameter, mm | Copper wire | Aluminum wire | ||||
| Current, A | power, kWt | Current, A | power, kWt | ||||
| 220 V | 380 V | 220 V | 380 V | ||||
| 0.5 mm2 | 0.80 mm | 6 A | 1.3 kW | 2.3 kW | |||
| 0.75 mm2 | 0.98 mm | 10 A | 2.2 kW | 3.8 kW | |||
| 1.0 mm2 | 1.13 mm | 14 A | 3.1 kW | 5.3 kW | |||
| 1.5 mm2 | 1.38 mm | 15 A | 3.3 kW | 5.7 kW | 10 A | 2.2 kW | 3.8 kW |
| 2.0 mm2 | 1.60 mm | 19 A | 4.2 kW | 7.2 kW | 14 A | 3.1 kW | 5.3 kW |
| 2.5 mm2 | 1.78 mm | 21 A | 4.6 kW | 8.0 kW | 16 A | 3.5 kW | 6.1 kW |
| 4.0 mm2 | 2.26 mm | 27 A | 5.9 kW | 10.3 kW | 21 A | 4.6 kW | 8.0 kW |
| 6.0 mm2 | 2.76 mm | 34 A | 7.5 kW | 12.9 kW | 26 A | 5.7 kW | 9.9 kW |
| 10.0 mm2 | 3.57 mm | 50 A | 11.0 kW | 19.0 kW | 38 A | 8.4 kW | 14.4 kW |
| 16.0 mm2 | 4.51 mm | 80 A | 17.6 kW | 30.4 kW | 55 A | 12.1 kW | 20.9 kW |
| 25.0 mm2 | 5.64 mm | 100 A | 22.0 kW | 38.0 kW | 65 A | 14.3 kW | 24.7 kW |
To find the required cable section in the corresponding column - 220 V or 380 V - we find a figure that is equal to or slightly more than the power we calculated earlier. We select the column based on how many phases are in your network. Single-phase - 220 V, three-phase 380 V.
In the found line, we look at the value in the first column. This will be the required cable cross-section for a given load (power consumption of devices). A cable with conductors of this cross section will have to be looked for.
A little about whether to use copper or aluminum wire. In most cases, when laying wiring in a house or apartmentuse copper cables. Such cables are more expensive than aluminum ones, but they are more flexible, have a smaller cross-section, and are easier to work with. But, copper cables with a large cross-section are no more flexible than aluminum ones. And with heavy loads - at the entrance to the house, to the apartment with a large planned power (from 10 kW and more), it is more expedient to use a cable with aluminum conductors - you can save a little.
How to calculate the current cable cross-section
You can choose the current cable cross-section. In this case, we carry out the same work - we collect data on the connected load, but look for the maximum current consumption in the characteristics. Having collected all the values, we sum them up. Then we use the same table. We are only looking for the nearest higher value in the column labeled "Current". In the same line we look at the cross-section of the wire.
For example, you need connect the hob with a peak current consumption of 16 A. We will lay a copper cable, therefore we look in the corresponding column - the third from the left. Since there is no value of exactly 16 A, we look in line 19 A - this is the nearest higher. Suitable cross-section 2.0 mm2... This will be the minimum cable cross-section for this case.

When connecting powerful household electrical appliances from shield pull a separate power line. In this case, the choice of cable cross-section is somewhat simpler - only one value of power or current is required
It is impossible to pay attention to a line with a slightly lower value. In this case, at maximum load, the conductor will be very hot, which can lead to the insulation melting. What could be next? May work circuit breakerif installed. This is the most favorable option. Household appliances may fail or a fire may start. Therefore, always make the choice of the cable cross-section according to the larger value. In this case, it will be possible later to install the equipment even a little more in power or current consumption without reworking the wiring.
Calculation of the cable by power and length
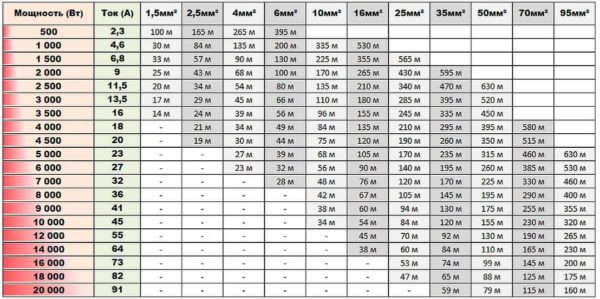
If the power line is long - several tens or even hundreds of meters - in addition to the load or current consumption, it is necessary to take into account the losses in the cable itself. Usually long distances of power lines with entering electricity from the pole into the house... Although all the data must be indicated in the project, you can play it safe and check. To do this, you need to know the allocated power to the house and the distance from the pole to the house. Further, according to the table, you can select the cross-section of the wire, taking into account the length loss.
In general, when laying electrical wiring, it is always better to take some margin over the cross-section of the wires. Firstly, with a larger cross-section, the conductor will heat up less, and hence the insulation. Secondly, more and more devices powered by electricity appear in our lives. And no one can guarantee that in a few years you will not need to install a couple of new devices in addition to the old ones. If stock exists, they can simply be turned on. If it is not there, you will have to be smart - or change the wiring (again) or make sure that powerful electrical appliances do not turn on at the same time.
Open and closed wire routing
As we all know, when current passes through a conductor, it heats up. The more current, the more heat is generated. But, when the same current passes through conductors with different cross sections, the amount of heat released changes: the smaller the cross section, the more heat is released.
In this regard, with an open laying of conductors, its cross section may be smaller - it cools faster, since heat is transferred to air. In this case, the conductor cools down faster, the insulation will not deteriorate. With a closed gasket, the situation is worse - heat dissipates more slowly. Therefore, for a closed gasket - in cable ducts, pipes, in the wall - it is recommended to take a cable with a larger section.
The choice of the cable cross-section, taking into account the type of its laying, can also be carried out using the table. The principle was described earlier, nothing changes. Another factor is simply taken into account.
And finally, a few practical tips. When going to the market for the cable, take a vernier caliper with you. Too often, the reported cross section does not match reality. The difference can be 30-40%, which is a lot. How does this threaten you? Burnout wiring with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, it is better to check right on the spot whether this cable really has the required core cross-section (diameters and corresponding cable cross-sections are in the table above). And in more detail about determining the section the cable by its diameter can be read here.












cable cross-section and conductor cross-section from 1mm2 and below 4 figure-table is clearly confused
Table for determining the cable cross-section by power and length - parameters for copper cable or for aluminum?