A vegetable garden for the lazy and smart: how to make comfortable and productive beds
A dacha and a vegetable garden, instead of a resting place, often become a place of exhausting work. Water, weed, loosen, water again, weed, loosen, and so on in a circle. At the same time, the harvest is not always happy. The situation can be changed. There is a special technology - a smart vegetable garden. The cultivated area decreases several times, the amount of water required for irrigation decreases, and the yield increases. This is not a fairy tale. Many have already switched to smart beds and they are all happy with the result.
The content of the article
What is a smart vegetable garden or smart beds
A smart vegetable garden allows you to get maximum yields with minimal labor costs. How? There are several basic rules and techniques: proper planting planning, turnover of planted plants, special growing technologies (in high beds, trenches), drip irrigation, mulching or the use of covering material. All this has been known for a long time and, for sure, is already used by many. But it is precisely in the complex that all these measures give what is called a “smart garden”. Because on the site everything is done according to the mind.
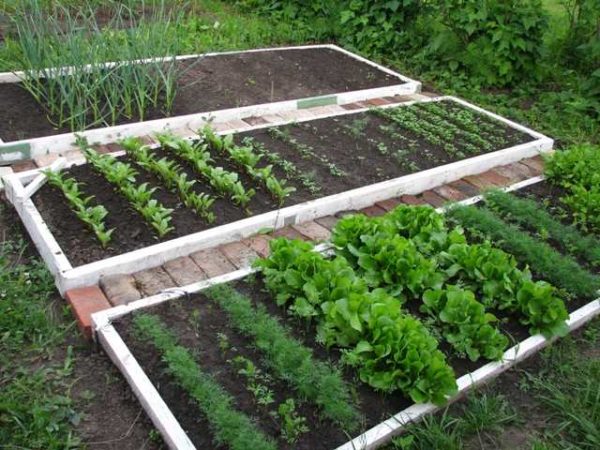

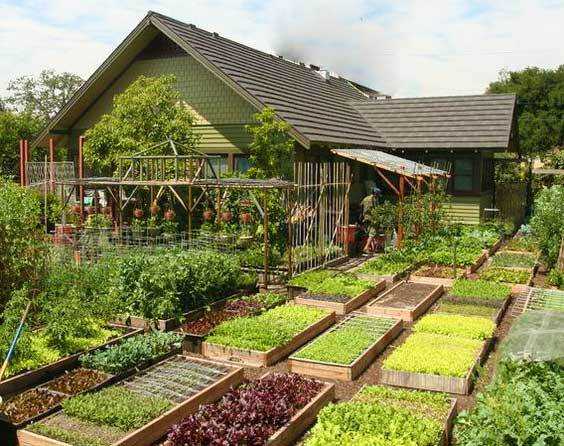
A smart vegetable garden is formed, often raised or high beds, in which the necessary conditions for plant growth are created
The main task of this technology is to do everything so that working in the country is not a heavy duty. This is possible if you approach the organization of the process wisely. And this technology is called “a vegetable garden for the lazy” for nothing. At the stage of arrangement, you will have to work hard, but then everything will grow almost by itself, but the first stage requires shock efforts.
It's worth starting with site planning. It is necessary to choose the location of the beds, taking into account the illumination. Then develop a scheme for laying along the section of water pipes and lay them. At the same time, you can deal with the device of the beds. In approximately this order. All this takes time, considerable effort and money. Material costs may not be too high.
We plan a vegetable garden
If you already have a summer cottage or a piece of land near your house, you have probably already faced a situation of an overabundance of fruits, vegetables and berries. When the harvest has to be distributed to relatives, neighbors, colleagues. But in order to grow it, it took a lot of effort. To avoid this situation, you need to plan your harvest. It is clear that you will not get great accuracy, but results close to the planned ones are possible.
We consider the area of the beds
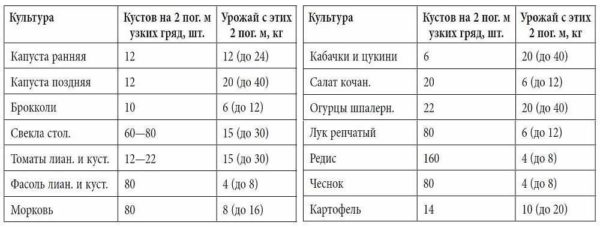
The first thing to do is sit down and think about what and how much you want to grow. Specific amount - in kilograms. How much do you need to "eat" and "close". Write down the list of plants (in a column) and the desired yield.
Having decided on the list of plants that you want to grow on your own, we sit down and look at the average yield that can be achieved when growing in smart beds. It is given in the table. Since you are still an inexperienced "lazy gardener", reduce it by half. We put down numbers opposite each of the plants. It should be recorded in kilograms per square meter of area.
Now it is easy to calculate how much area you need to allocate for each type of plant: we divide the desired yield in kilograms by the average yield for each type of plant. We get the square footage for vegetables, berries, herbs, etc.If we add all these areas, we find out how many beds you need in total. These are the beds that need to be placed on your site.
Chances are you are surprised at how little space you need for your beds. And the truth is not enough. At times less than what we are used to! In processing, you will have very little land. The vacated space can be taken under flower beds, rockeries, fountains and other decorations.
Where to locate
When planning smart beds, you need to take into account the degree of illumination. Almost all plants you need prefer sunny locations. In partial shade, you can grow rhubarb, sorrel, onions (including feathers). Perhaps that's all. There are no garden plants that grow well in shaded areas. Rather, they will grow, but the yield will decrease by 3-4 times. Shady areas should be set aside for a recreation area or place a flower bed with shade-loving plants there.
Another principle for placing beds: the more care (read watering) the culture requires, the closer to the entrance to the house it must be located:
- There should be a greenhouse with seedlings right next to the exit.
- Nearby - a garden for radish, salad.
- Immediately or a little further - tomatoes, cucumbers, herbs.
- Even further - peppers, eggplants, cabbage of various types, beans, root vegetables.
- At the back are potatoes, pumpkin, squash, corn, sunflowers and perennials.
- The garden is farthest.
Why arrange plants this way? Because at the beginning of the watering / weeding work, the gardeners are full of enthusiasm and the plants get more water, the weeds are removed more thoroughly. Gradually, the ardor subsides, less and less water per square of area gets, the processing becomes less thorough. And with the approach suggested above, the amount of water will be “just right” and with tillage everything will be fine.
Orientation to the cardinal points and precise location
If you want to harvest from the entire area of a lazy garden, the location is north-south. Strictly. Only in this way the whole area will bear fruit. Also place the trellis for curly vegetables. Although, they can be planted along the southern and eastern walls of buildings.
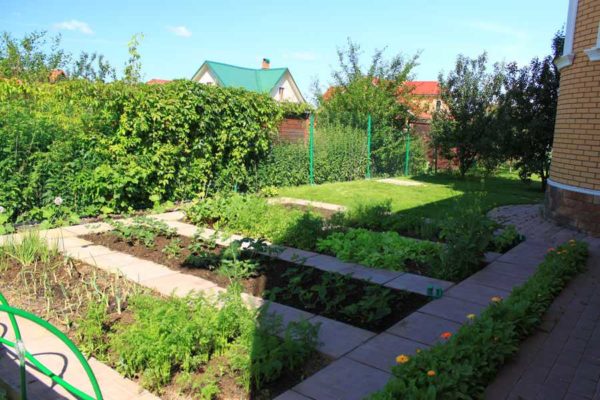
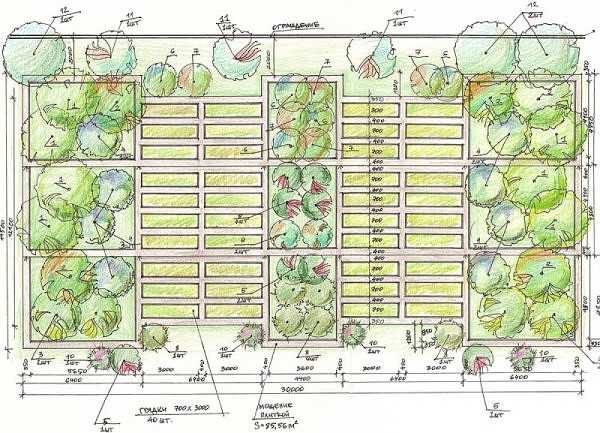
In order for a smart garden to be also beautiful, you need to think about where to put the beds. To do this, take a plan of the site on a scale indicating the direction to the north / south. On it we draw all the buildings and capital paths, water supply (we pay special attention to the position of the taps), trees and shrubs. On the plan we immediately outline the shadow zones - we will not place vegetables here, this is a place for flowers, gazebos, fountains.
Cut out the beds from paper (on the same scale as the site plan). And we make them in the shape that we plan: rectangle, square, circle, triangle, etc. The form is chosen based on the area planned for the culture. And it doesn't have to be a boring rectangle. Since there will be enough free space (you remember that much less beds are needed), then rationalism fades into the background, and we focus on aesthetics. After all, few people work in the country "so that there is something to eat", mostly it is also a pleasure. And what could be more pleasant than the beauty of the cultivated area?
So, we sign each piece of paper denoting a smart bed - we put the name of the culture or crops (you can grow two or three or more on one bed). Now we are looking for a place for each, taking into account the rules described above. Along the way, you can change the shape of smart beds: for the sake of beauty or convenience. When you have found the places, draw the contours, transfer the inscriptions. It remains only to realize our plans.
Irrigation system
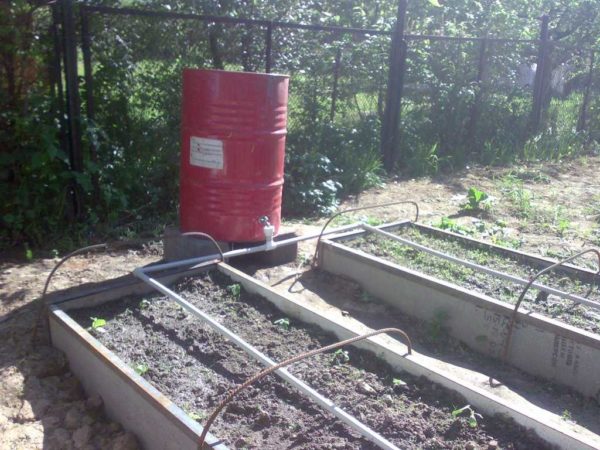
A significant part of the work in the garden is watering the plants. If you use lazy beds, you will need to water much less often. But even in this case, it is better to do the piping around the site correctly. You already have a plan for the location of the beds in your garden.Now add flower beds, bushes and trees there. Get a layout plan for the plants to water. Now you should think about how lay water pipes in the vegetable gardenso that to any "object of irrigation" was no more than 2-3 meters. If you do this, then you will have to pull a small hose to each bed, which is much easier.
It is even better if a drip hose is installed in the smart garden. This will reduce water consumption and increase yields. Yes, at the same time. The drip hose is a polyethylene tube with small holes through which water drips out. When planting, the plants are planted next to the holes. As a result, the water is supplied under the root, the plant receives a sufficient amount of moisture, and the gaps between the plants remain only slightly moist (due to the redistribution of moisture in the soil).
When using drip irrigation, you will have very little work. You open the tap, wait a certain period of time, turn off the tap. All. Drip irrigation hoses are available for connection to the water supply (sold per meter), available in sets with a small pump that will pump water from the tank. The run-up in prices for hoses for drip irrigation is solid - prices differ significantly. As limited as your finances are, don't go for the cheapest hoses - they won't last more than one season. It is better to overpay a little for a quality product and use it for several years. When choosing drip irrigation kits, you should also look at the irrigated area. But, most likely, it will suit you, since lazy beds are rarely large. Read more about drip kits and manufacturers. here.
How to make smart / lazy garden beds
The principle of building smart / lazy beds is that you need to create ideal conditions for the development of plants and the convenience of processing for yourself. What do plants need? Nutrients, sufficient light, air, moisture and no weeds.
Oxygen and nutrients
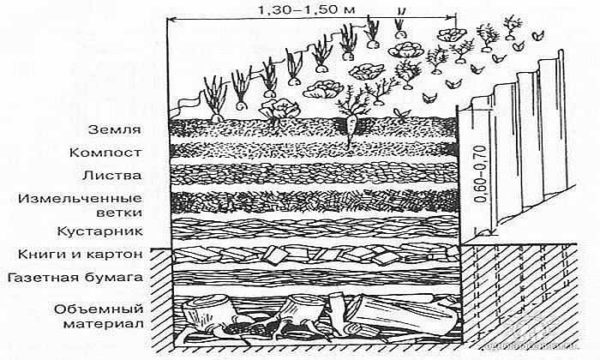
We provided enough sun for them by arranging the beds from north to south. The next task is nutrients and air to the roots. We lay all this when forming the beds. Depending on the type of soil, we select the components that are lacking in the "source material". In Central Russia, the main soils are clay and loam, so humus of varying degrees of "maturity" (a year, two and three) is usually added. This is both for fertilization and for lightening the soil - for better oxygen access to the roots. Together with humus, bacteria and worms enter, which continue processing, enriching the soil and loosening it for you.
If necessary, you can apply other fertilizers - in the holes when planting or when watering. Depends on crops or wealth / poverty of source soils. The most common natural fertilizers are chicken manure and cow dung, and ash. When you apply only cow dung, you will be annoyed by bears. If you add a little chicken droppings, there will be no bear, and the composition of the soil will become richer.
Moisture retention and weed control
Moisture will be partly delivered by rain and dew, partly will have to be added by watering. And so that less water is required, the entire space of the garden is not filled with plants, we fill it with mulch. Mulch, by the way, also reduces the number of weeds - there is not enough light for them under it.
As mulch can be used straw, grass cuttings, sawdust, fallen needles, special mulch made from wood chips. All of this can be used to mulch lazy beds. But all materials are imperfect. Here are their advantages and disadvantages:
- The straw quickly decays.On the one hand, it is good - the enrichment of the soil, on the other - you have to renew it about once a month.
- Cut grass and plant debris. The disadvantage is the same - they quickly rot, but still look "not very". In addition, only the grass is suitable, in which there are no seeds and "sores", otherwise you will have violent shoots of fresh grass and a lot of problems with diseases.
- Sawdust. Large ones are more suitable - they look better. Fresh sawdust is not recommended to use, as they acidify the soil. Mulch should be two or three years old (pile up and store).
- Fallen needles. Excellent mulch. It looks beautiful, does not rot for a long time, contains a lot of bacteria and fungi useful for the soil.
- Wood mulch. It is obtained by processing branches and trunks of young trees. This is an excellent material for mulching a vegetable garden, but if you buy it, it turns out to be expensive. But you can do it yourself. You probably have trees, bushes, vines. After pruning, you have to come up with something with cut branches. In the presence of garden shredder, you solve this problem, and even provide your lazy vegetable garden with first-class mulch.
There is another good way out: cover smart / lazy beds with a special black covering material. They completely cover the surface of the beds, sometimes in two layers. Small holes are made under the plants. Watering is carried out directly on the material - it does not retain water and air, does not allow weeds to grow, and protects the soil from overheating. In general, everyone is good, except that you have to buy it.
How to make them
We figured out the general principles of creating a smart garden, now we will specifically figure out how to make beds. You cannot walk on them, so they must be fenced off - with stones, slate, iron, logs sawn in half, boards ... It doesn't matter what, but the beds must be separated from the paths. And since you cannot step on the beds, their width should be such that you can freely work the soil.
Now about the width of the smart beds. It depends on the type: will they be of regular height or raised. If the beds are made at ground level, their width is 80-100 cm. Squatting or bending over, you can process such a width. If the beds are raised even half a meter, it will be even more convenient to work. They make not only high beds. All possible growing technologies can be used:
- Container beds. Their parameters: width up to 1 meter, height - 30-40 cm or 70-80 cm, length - any. Fenced can be any material.
- Bed-box. It is indispensable for the northern regions, since the soil warms up faster in the box-bed. It differs in lower height - 15-20 cm, width 100-120 cm. Plants can be planted in any direction - along or across (but the rows must be placed from north to south).
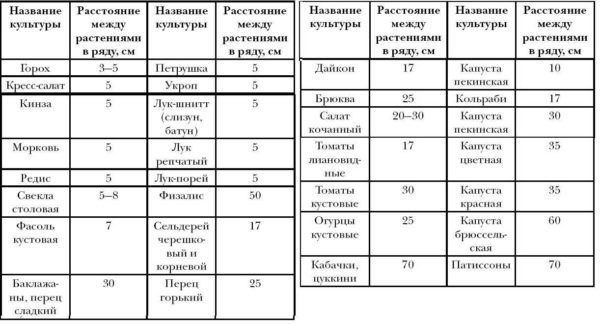
- Narrow beds. The width of the beds is up to 0.5 meters, the row spacing is -1 m. May be at ground level, but the row spacing must be highlighted. Vegetables are planted in two rows in a checkerboard pattern.
- The beds in the barrel. These are especially good for climbing plants: cucumbers, squash, pumpkin.
- Pit beds and ditches.
- Vertical.
Now about whether the usual height of the beds is better or raised. For a really lazy garden, raised ones are better: you will have to work less when working the soil. But arrangement of high beds - a troublesome and slow business. So for a start, you can acquire high beds only for the most difficult crops to care for. And you can also use various containers / containers - for herbs, salads, spicy plants. Large barrels and boxes sawn along are suitable. There are plastic containers on sale that are made specifically for the smart garden. They can generally be placed on the paths near the entrance to the house.
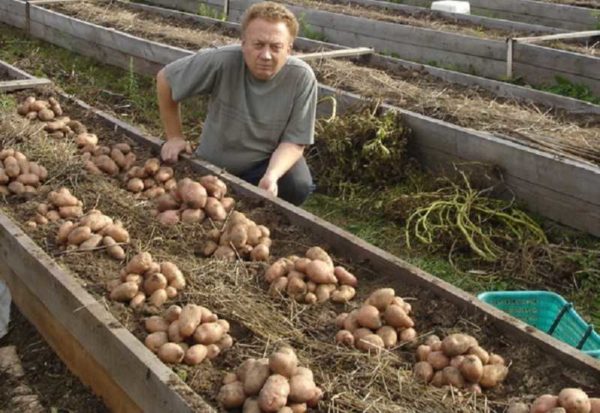
The only crop for which raised beds should not be made is potatoes.It grows well in trenches, and it is much easier and faster to make them.
Between the beds
The beds in the smart garden are separated, the distance between them is at least 60 cm (preferably 90-100 cm or more). A solid distance that needs to be filled with something. Weeding between the beds is not a good idea. Why then bother with individual beds to fight the weeds between them ... Therefore, you can either lay out / pave track or sow lawn grass. The best grass for our lawn is bluegrass and red grass. They grow quickly, form dense greenery that does not trample and even tolerates work with a cart.

In order not to weed the space between the beds, it can be sown with lawn grass. And beautiful and no dirt
The grass will need to be cut, so you need a lawn mower or trimmer. And the cut grass can be used for mulch. Then, by the way, weeds will emerge - they cannot withstand frequent haircuts.
Some tricks
The technology is called smart vegetable garden for good reason. You can test different approaches, novelties, experience of "colleagues". There are a few tricks that come with use. We have already talked about one - about the covering material. It really makes maintenance a lot easier and you don't need mulch. There are more interesting ideas:
- After crops "heavy" for the earth, sow oats, peas, mustard, rapeseed. After a couple of weeks, juicy greens grow. You can leave it "under the snow", dig it up in the spring. Or dig up just before the snow, along with the greenery. The purpose here is twofold - young greens rotting, enriching the land. This time. And two - weeds do not grow, as the seedlings are friendly.
- Use white covering material to extend the summer season and get an early harvest. Arcs are made from a steel rod with a diameter of 8-1o mm. In medium or high density spunbond, drawstrings are sewn with a width of 2 cm or more. Arcs are pushed into them, spunbond is assembled on the wire so that the ends of the wire are free. The portable mini greenhouse is ready. Stick arcs from both ends of the garden. To close the plants from frost, spread the spunbond, you can open it for a day, collecting all the material on one side. The same design will save you from overheating in the summer heat.
- Place a large metal barrel in the corner of the lot. Weeds and other plant waste should be put into it. To fill with water. The greens will quickly rot and this slurry can be used for feeding. Only the barrel needs to be covered - the contents do not smell the best.
Surely there are more tricks in the processing of a smart vegetable garden. If we find out about them, we will definitely supplement the article.