Polyethylene pipes: marking, diameters, characteristics, application
If earlier, when installing a water supply system, sewage, when conducting gas, only metal or cast iron pipes were always used. There was simply no alternative. Today, polymer products are increasingly used, and, in particular, polyethylene pipes. They are increasingly displacing metal counterparts from the market, and all due to their low price, ease of use, and a long service life. The ease of installation adds polarity to PE pipes - there are fittings that are installed by hand. This is very convenient, for example, when installing a water supply system or an irrigation system in the country.

Plumbing made of polyethylene pipes is easy to assemble, easy to upgrade, and requires almost no maintenance
The content of the article
Properties, advantages, disadvantages
Polyethylene pipes are used to transport various liquid and gaseous substances. In the literature, you can find an abbreviation: in the Russian version it is PE, in the international version - PE or PE-X for cross-linked polyethylene.
They have excellent properties:
- The material is chemically neutral and does not react even with hydrochloric acid. Thanks to this, they are used in production processes.
- Normally, it does not emit any substances, does not affect the taste of the transported liquids. This allows them to be used in the construction of pipelines through which liquids circulate that can be consumed.
- The inner walls of polyethylene pipes are very smooth, no substances are retained on them. Even after many years, there will be no deposits on them.
- Smooth walls offer less resistance to water flow. Less resistance - less powerful pump is required for pumping, less energy is spent.
- Service life under normal operating conditions is about 50 years. But this figure decreases sharply with increasing temperature or pressure.
- Easy to cut, lightweight, easy to install.
- They do not conduct currents, do not corrode.
- Polyethylene pipes with a diameter of up to 160 mm can be connected using special fittings. They are simply installed without any equipment, which is convenient in "field conditions", for example, in the country. Large diameters are welded with a special machine, but they are usually used in industry.
- Polyethylene conducts sounds poorly. So such a pipeline or heating system is "quiet".
- The price of a polyethylene pipeline is 30-40% cheaper than a similar steel one.
- An already finished plumbing or heating system is easy to remodel. In the right place, the pipe is cut, the required fitting is installed, to which you can connect another branch or some device.
An excellent set of properties has led to the fact that polyethylene pipes become more and more popular. But in order to avoid surprises, you need to know their shortcomings. There are not many of them, but they are quite serious.
- Polyethylene burns and emits harmful substances during combustion.
- Weak resistance to ultraviolet light. The material becomes brittle and brittle when exposed to the sun. But pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene are not susceptible to this disease, they have become the sales leaders lately.
- Large thermal expansion - 10 times that of steel. To neutralize this disadvantage, a compensator is installed.
- If the liquid in the pipeline freezes, the polyethylene can break.Therefore, when using polyethylene pipes to organize water supply for a private house or summer cottage, it is laid below the depth of freezing or insulated from above, additional heating methods are used (heating cables).
These are all disadvantages. Now about the varieties. According to the production method, there are three types of polyethylene pipes:
- high pressure;
- low pressure;
- made of cross-linked polyethylene (often red, since in most cases they are used for laying heating and hot water systems).
There is a certain paradox in these names. When we talk about high or low pressure polyethylene pipes, they mean the way they are produced. But this is often perceived as an area of use. In reality, the opposite is true. Pipes produced at high pressure are less durable. They can only be used for gravity systems (no pumps). For pressure water supply systems, they are made, but strength is gained due to the thickness of the walls. With the usual wall thickness, their area of use is sewage, drainage systems, storm drains, etc. Here their qualities are optimal.
In pressure pipelines, where there is high pressure, low-pressure polyethylene pipes are used. They are more durable but, at the same time, more fragile, bend much worse. This is also not very good. But they can withstand significant pressure drops without any harm. And I must also say that both of these types of polyethylene pipes are suitable only for cold water - they cannot withstand hot water, they can melt.
But the third type - made of cross-linked polyethylene - is an option with high strength and flexibility. Such products withstand high pressure (up to 20 atm) and temperatures up to + 95 ° C, that is, PE-X pipes can also be used for hot water supply, as well as for heating systems. By the way, metal-plastic pipes are made of this type of polymer. However, there is one "but" here - this type of material is not welded. When installing a XLPE pipeline, fittings with gaskets are used. The second type of assembly is adhesive, when the joints of the elements to be joined are coated with glue.
Markings and diameters
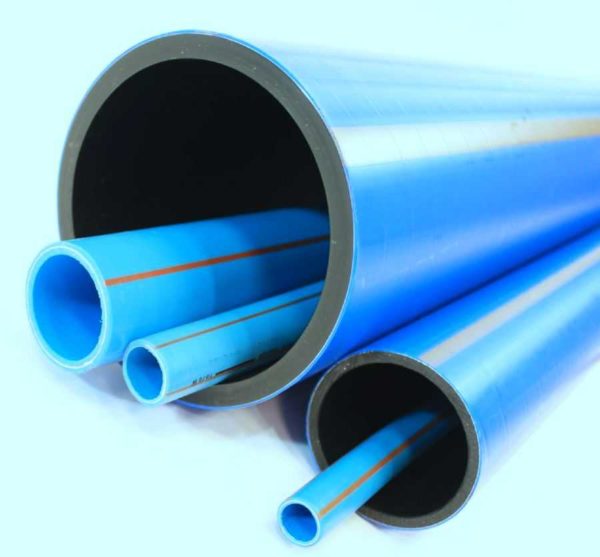
Polyethylene pipes are usually black or bright blue, and XLPE pipes can be bright red. They are colored in this way on purpose - so that it is easier to distinguish them from other polymers. On the wall, stripes of blue color can be applied along if it is intended for cold water, yellow if it is used for a gas pipeline. The form of release - in coils with a length of 20 to 50 meters (usually small diameters) and pieces of 12 meters (or the required length by agreement).
The diameters of polyethylene pipes vary in a wide range - from 20 mm to 1200 mm. Small-section products (up to 40 mm) are mainly used for water supply and heating systems in private houses and apartments, more serious ones (up to 160 mm) go to the risers of water supply, heating and sewerage systems. Large diameters are already an industrial and manufacturing area. Practically not used for private buildings and apartments.
Density of polyethylene
For the manufacture of pipes, polyethylene of different density is used. The density is indicated by the numbers that stand after the abbreviation:
- PE32 - appeared first, has the lowest density. Today it is practically not used for the production of pipes.
- PE63 - has a rather large distance between the chains of molecules, which is why it does not tolerate pressure surges poorly and can break. Scope - internal wiring in non-pressure systems (irrigation systems from a barrel, Summer shower etc.), occasionally placed in private houses for wiring the water supply system inside the house. Sewer systems can be made of this type of polymer.
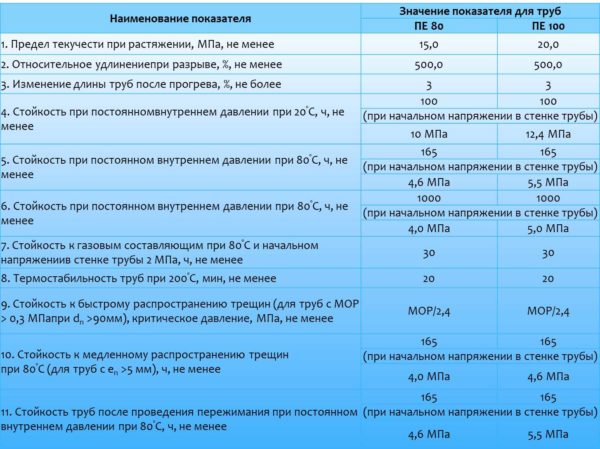
- PE80 - has high strength, can be used in cold water supply systems inside and outside the house, but with mandatory insulation. With large wall thickness, they can be used for industrial purposes.
- PE100. At the moment, pipes made of this material are the most durable, but also the heaviest. It can be used in any field, for transporting liquids and gases under high pressure. The grades are made of cross-linked polyethylene with a density of 100, can be used in the distribution of hot water and heating.
What else may be interesting: polyethylene pipes can also be reinforced. In general, they are produced by the extrusion method - in a softened state, the material is squeezed out through a nozzle, then sent to calibration, where it is given the required section and size. In the production of reinforced polyethylene pipes, fibers of nylon, polystyrene or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are sealed inside the wall. The equipment for this process is much more complex, and therefore the price for reinforced PE pipes is much higher.
Diameter of polyethylene pipes and what is SDR
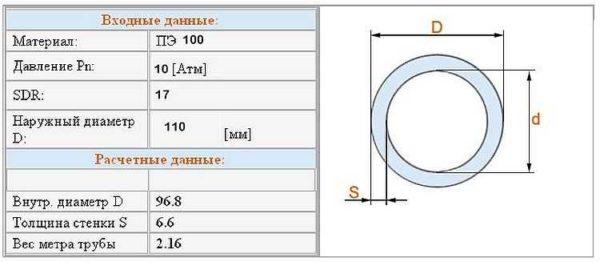
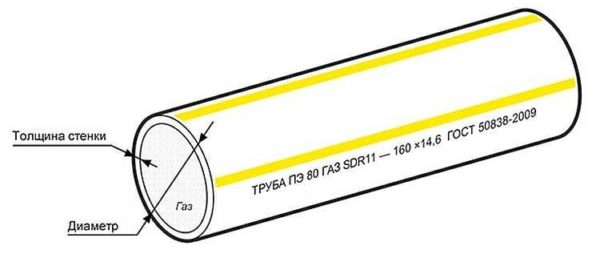
There is a significant difference in the marking of polymer pipes - the outer diameter is indicated. But the wall thickness varies within wide limits, so the inner diameter has to be calculated - from the outer one subtract twice the wall thickness. The wall thickness in the marking is prescribed after specifying the outer diameter (usually * or "x" sign). For example: 160 x 14.6. This means that this pipe has an outer diameter of 160 mm, a wall thickness of 14.6 mm. The inner diameter of the polyethylene pipe can also be calculated: 160 mm - 14.6 mm * 2 = 130.8 mm.
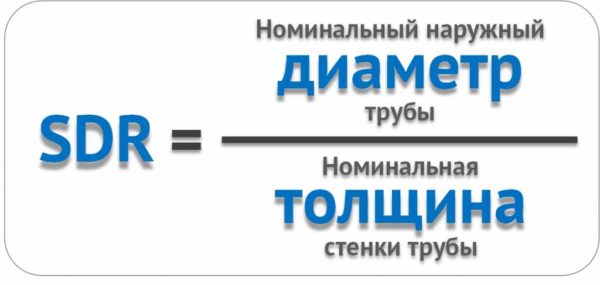
Also in the marking there is an abbreviation SDR and some numbers. The numbers are the ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thickness. This indicator reflects the strength of the walls and their ability to withstand pressure surges.
The lower the SDR, the more durable (but also heavier) the pipe is. True, this is true within products of the same density. For example, PE 80 SDR11 is stronger than PE 80 SDR 17.
| PE pipe name | Specifications | Application area |
|---|---|---|
| PE 63 SDR 11 | Low density, poorly tolerate temperature changes | Internal cold piping |
| HDPE PE-63 SDR 17.6 | GOST 18599-2001 (2003), pressure not higher than 10 atm | Internal low pressure water lines for cold water supply |
| PE 80 SDR 13.6 | The density is higher, but temperature changes do not tolerate well | Cold water pipes, irrigation systems |
| PE 80 SDR 17 | The density is higher, but temperature drops | Water pipes both indoors and outdoors, pressure irrigation systems |
| PE 100 SDR 26 | High density, ability to withstand temperature changes | Any pipelines for transporting liquids (water, milk, juice, etc.) |
| PE 100 SDR 21 | Increased wall thickness | Any pipelines, including gas |
| PE 100 SDR 17 | Increased wall thickness, but also a large mass | More often used for industrial purposes |
| PE 100 SDR 11 | Low pressure polyethylene, high strength, increased chemical resistance | Can be used for the installation of sewers, laid in any type of soil |
Pipe series and pressure ratings
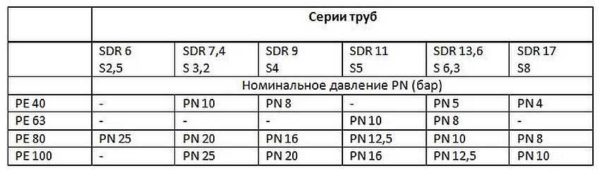
The next parameter that may be important when choosing is a series. It is designated by the letter S followed by numbers. Displays the ability of the walls to resist pressure. This is the ratio of the pressure that it can withstand (determined in laboratory conditions) to the working one. The higher the number, the stronger the pipe.
In practice, this indicator is rarely taken into account, as it is more "laboratory" than practical. Much more important may be the pressure rating for which the walls are designed. These data are presented in the photo above. The pressure is at the intersection of columns and rows, indicated in Atmospheres.For example, for a PE 80 SDR 13.6 pipe, the operating pressure is PN10 (10 atm). This means that when transporting media with a temperature of no more than + 20 ° C and a pressure of no more than 10 atm, the service life of this pipe is 50 years.
Regulations
For the standardization of products, GOSTs and industry standards were developed. The regulatory framework for this type of materials appeared not so long ago - already in the current millennium - after 2000. The labeling usually indicates the standard that the given type of product meets. According to the name of GOST, the scope is determined (from the names of GOSTs), but it is easier for non-professionals to be guided by the presence of stripes of the corresponding color (blue - for cold water, yellow - for gas).
Here are the standards for Russia:
- GOST 18599-2001 Polyethylene pressure pipes.
- GOST R 50838-2009 Polyethylene pipes for gas pipelines.
- GOST R-2008 Multilayer pressure pipes for water supply and heating systems.
- GOST 32415-2013 Thermoplastic pressure pipes and fittings for them for water supply and heating systems. General specifications
There are standards for Ukraine:
- DSTU B V.2.7-151: 2008 "Polyethylene pipes for cold water supply"
- DSTU B V.2.5-322007 "Non-pressure pipes made of polypropylene, polyethylene, non-plasticizable polyvinyl chloride and fittings for them for external sewerage networks of houses and structures and cable ducts"
- DSTU B V.2.7-73-98 "Polyethylene pipes for the supply of combustible gases"
All of them can be studied if desired. Most of them are tables in which the entire assortment of products is indicated with an indication of the parameters.
Example of PE pipe marking
For identification purposes, polyethylene pipes are marked. The inscriptions are applied on every meter or so. The first is the name of the manufacturer, maybe the campaign logo. This sign is optional, but it is a good sign - the company is not afraid for its goods.
Followed by:
- designation of the pipe material, in this case - PE - polyethylene;
- the density of the polyethylene is for this example 80;
- then SDR pipes - 11;
- the next is the outer diameter and wall thickness: 160 mm pipe diameter, 14.6 mm - wall thickness;
- the last position indicates GOST or DSTU, which corresponds to this type of pipe.
The pipe shown in the photo - for gas pipelines this is underlined three times - with yellow stripes, the inscription "gas" in the marking and the name of GOST - 50838-2009 - this is the standard by which plastic pipes for gas pipelines are produced.